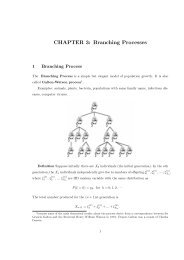
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
CHAPTER 2: Markov Chains (part 3)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
we have<br />
v 2 = 13.3333, v 3 = 6.3333, v 4 = 16.3333<br />
is<br />
Example[understanding T] Consider a <strong>Markov</strong> Chain whose transition probability matrix<br />
P =<br />
1 2 3<br />
1 a b c<br />
2 d e f<br />
3 0 0 1<br />
The MC starts at time 0 with X 0 = 0. Let T = min{n ≥ 0 : X n = 3} Find P (X 3 = 0|X 0 =<br />
0; T > 3)<br />
Example [understanding one-step analysis] Consider a <strong>Markov</strong> Chain whose transition probability<br />
matrix is<br />
P =<br />
The MC starts at time 0 with X0 = 2.<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
1 1 0 0 0<br />
2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.4<br />
3 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.1<br />
4 0 0 0 1<br />
1. What is the probability that when the process is absorbed, it does so from state 2?<br />
2. What is the probability that when the process is absorbed by state 4, it does so from state<br />
2?<br />
8