Dimensional Measurement using Vision Systems - NPL Publications ...
Dimensional Measurement using Vision Systems - NPL Publications ...
Dimensional Measurement using Vision Systems - NPL Publications ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Measurement</strong> Good Practice Guide No. 39<br />
The angle of view is important as it defines the physical position of the lens and camera.<br />
The angle of view can be expressed as:<br />
β = 2 tan -1 ( b/2f )<br />
…..(11)<br />
4.1.3 Depth of field<br />
Equation 7 indicates the relationship between the focal length and the object and image<br />
distances for a single thin lens where it is assumed that the lens dimensions do not affect<br />
the formation of the image. In this case there is only one image distance at which an object<br />
will appear in focus for a given object distance and focal length. In reality, the lens<br />
dimensions do affect the image and a typical camera lens will consist of several lenses.<br />
With such lens assemblies there will be a range of object distances at which there will be<br />
no discernable defoc<strong>using</strong> of the image.<br />
As we are imaging on to a CCD camera, we may consider the object’s depth to be a series<br />
of points, with any given point, half the size of one pixel. Selecting the point size as half a<br />
pixel means that it cannot illuminate two pixels at the same time. The point is out of focus<br />
if it does not appear as a point (i.e. it is imaged as greater in size than 1 pixel). On the<br />
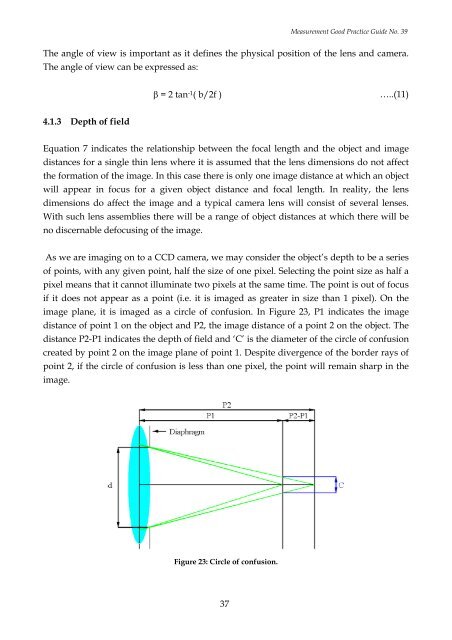
image plane, it is imaged as a circle of confusion. In Figure 23, P1 indicates the image<br />
distance of point 1 on the object and P2, the image distance of a point 2 on the object. The<br />
distance P2-P1 indicates the depth of field and ‘C’ is the diameter of the circle of confusion<br />
created by point 2 on the image plane of point 1. Despite divergence of the border rays of<br />
point 2, if the circle of confusion is less than one pixel, the point will remain sharp in the<br />
image.<br />
Figure 23: Circle of confusion.<br />
37