Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.2.<br />
Direct-acting solenoid<br />
<strong>valves</strong>: plungers<br />
General characteristics:<br />
■ Rugged design<br />
■ Good value for money<br />
■ Universal field of application<br />
■ Broad nominal diameter range<br />
■ AC, DC and UC variants available<br />
■ Friction leads to restricted service<br />
life without lubrication<br />
■ Restricted pressure range results<br />
from media separation<br />
■ On 3/2-way version, one port points<br />
upwards<br />
■ Circuit function B (normally open),<br />
available for many versions<br />
■ Also available as explosion-proof<br />
version<br />
■ With push-over coil.<br />
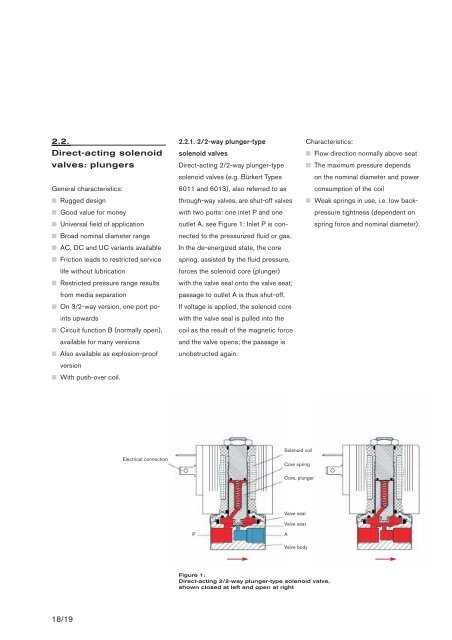
2.2.1. 2/2-way plunger-type<br />
solenoid <strong>valves</strong><br />
Direct-acting 2/2-way plunger-type<br />
solenoid <strong>valves</strong> (e.g. Bürkert Types<br />
6011 and 6013), also referred to as<br />
through-way <strong>valves</strong>, are shut-off <strong>valves</strong><br />
with two ports: one inlet P and one<br />
outlet A, see Figure 1: Inlet P is connected<br />
to the pressurized fluid or gas.<br />
In the de-energized state, the core<br />
spring, assisted by the fluid pressure,<br />
forces the solenoid core (plunger)<br />
with the valve seal onto the valve seat;<br />
passage to outlet A is thus shut-off.<br />
If voltage is applied, the solenoid core<br />
with the valve seal is pulled into the<br />
coil as the result of the magnetic force<br />
and the valve opens; the passage is<br />
unobstructed again.<br />
Characteristics:<br />
■ Flow direction normally above seat<br />
■ The maximum pressure depends<br />
on the nominal diameter and power<br />
consumption of the coil<br />
■ Weak springs in use, i.e. low backpressure<br />
tightness (dependent on<br />
spring force and nominal diameter).<br />
<strong>Solenoid</strong> coil<br />
Electrical connection<br />
Core spring<br />
Core, plunger<br />
Valve seal<br />
Valve seat<br />
P<br />
A<br />
Valve body<br />
Figure 1:<br />
Direct-acting 2/2-way plunger-type solenoid valve,<br />
shown closed at left and open at right<br />
18/19