Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Solenoid valves - Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1. <strong>Solenoid</strong> systems for solenoid <strong>valves</strong><br />
1.1.<br />
Basics<br />
<strong>Solenoid</strong> <strong>valves</strong> are the most frequently<br />
used control elements in fluidics.<br />
Their tasks are to shut off, release,<br />
dose, distribute or mix gases and fluids.<br />
They are confronted with many different<br />
requirements in your application<br />
areas, e.g.<br />
■ fast and safe switching<br />
■ high reliability<br />
■ long service life<br />
■ good medium compatibility of the<br />
materials used<br />
■ low control power<br />
■ compact design.<br />
Besides the plunger-type actuator<br />
which is used most frequently, pivotedarmature<br />
actuators and rocker actuators<br />
are also used.<br />
1.2.<br />
The basic operating<br />
principle of a solenoid<br />
While the actuation system, mechanical<br />
construction and the function as a<br />
whole do indeed differ, fundamental<br />
elements of the actuator are identical<br />
on virtually all actuation principles. The<br />
core of a solenoid consists of an electrical<br />
magnet, which is also referred to<br />
as a solenoid coil.<br />
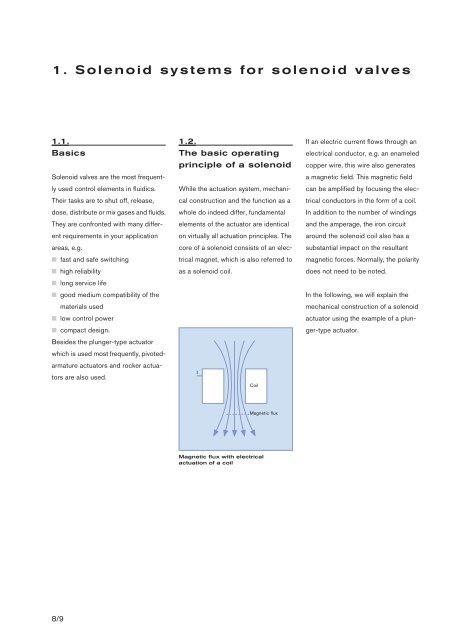
I<br />
Coil<br />
If an electric current flows through an<br />
electrical conductor, e.g. an enameled<br />
copper wire, this wire also generates<br />
a magnetic field. This magnetic field<br />
can be amplified by focusing the electrical<br />
conductors in the form of a coil.<br />
In addition to the number of windings<br />
and the amperage, the iron circuit<br />
around the solenoid coil also has a<br />
substantial impact on the resultant<br />
magnetic forces. Normally, the polarity<br />
does not need to be noted.<br />
In the following, we will explain the<br />
mechanical construction of a solenoid<br />
actuator using the example of a plunger-type<br />
actuator.<br />
Magnetic flux<br />
Magnetic flux with electrical<br />
actuation of a coil<br />
8/9