Part 1 - English version (PDF) - Convention on Biological Diversity
Part 1 - English version (PDF) - Convention on Biological Diversity
Part 1 - English version (PDF) - Convention on Biological Diversity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
India’s Fourth Nati<strong>on</strong>al Report to the <str<strong>on</strong>g>C<strong>on</strong>venti<strong>on</strong></str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> <strong>Biological</strong> <strong>Diversity</strong><br />
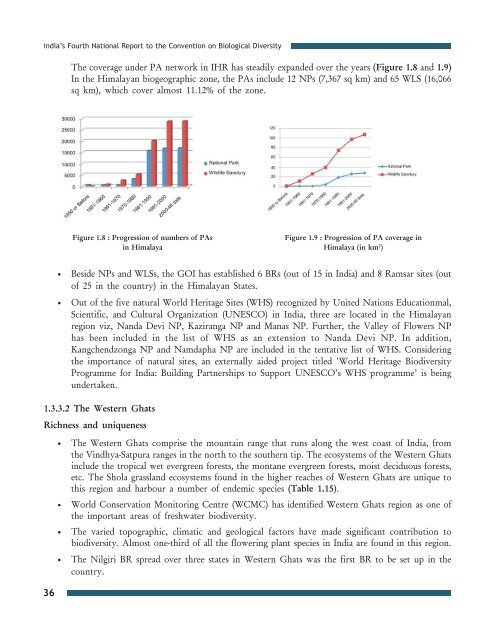
The coverage under PA network in IHR has steadily expanded over the years (Figure 1.8 and 1.9)<br />
In the Himalayan biogeographic z<strong>on</strong>e, the PAs include 12 NPs (7,367 sq km) and 65 WLS (16,066<br />
sq km), which cover almost 11.12% of the z<strong>on</strong>e.<br />
Figure 1.8 : Progressi<strong>on</strong> of numbers of PAs<br />
in Himalaya<br />
Figure 1.9 : Progressi<strong>on</strong> of PA coverage in<br />
Himalaya (in km 2 )<br />
<br />
<br />
Beside NPs and WLSs, the GOI has established 6 BRs (out of 15 in India) and 8 Ramsar sites (out<br />
of 25 in the country) in the Himalayan States.<br />
Out of the five natural World Heritage Sites (WHS) recognized by United Nati<strong>on</strong>s Educati<strong>on</strong>mal,<br />
Scientific, and Cultural Organizati<strong>on</strong> (UNESCO) in India, three are located in the Himalayan<br />
regi<strong>on</strong> viz, Nanda Devi NP, Kaziranga NP and Manas NP. Further, the Valley of Flowers NP<br />
has been included in the list of WHS as an extensi<strong>on</strong> to Nanda Devi NP. In additi<strong>on</strong>,<br />
Kangchendz<strong>on</strong>ga NP and Namdapha NP are included in the tentative list of WHS. C<strong>on</strong>sidering<br />
the importance of natural sites, an externally aided project titled 'World Heritage Biodiversity<br />
Programme for India: Building <str<strong>on</strong>g>Part</str<strong>on</strong>g>nerships to Support UNESCO’s WHS programme’ is being<br />
undertaken.<br />
1.3.3.2 The Western Ghats<br />
Richness and uniqueness<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
The Western Ghats comprise the mountain range that runs al<strong>on</strong>g the west coast of India, from<br />
the Vindhya-Satpura ranges in the north to the southern tip. The ecosystems of the Western Ghats<br />
include the tropical wet evergreen forests, the m<strong>on</strong>tane evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests,<br />
etc. The Shola grassland ecosystems found in the higher reaches of Western Ghats are unique to<br />
this regi<strong>on</strong> and harbour a number of endemic species (Table 1.15).<br />
World C<strong>on</strong>servati<strong>on</strong> M<strong>on</strong>itoring Centre (WCMC) has identified Western Ghats regi<strong>on</strong> as <strong>on</strong>e of<br />
the important areas of freshwater biodiversity.<br />
The varied topographic, climatic and geological factors have made significant c<strong>on</strong>tributi<strong>on</strong> to<br />
biodiversity. Almost <strong>on</strong>e-third of all the flowering plant species in India are found in this regi<strong>on</strong>.<br />
The Nilgiri BR spread over three states in Western Ghats was the first BR to be set up in the<br />
country.<br />
36