Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
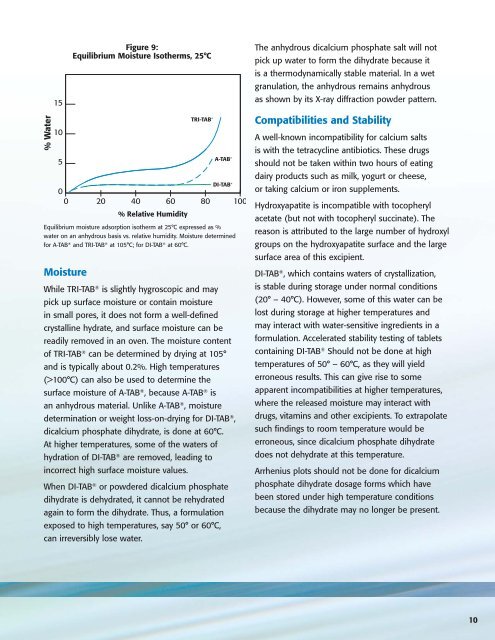
% Water<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
Moisture<br />
Figure 9:<br />
Equilibrium Moisture Isotherms, 25°C<br />
0<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100<br />
% Relative Humidity<br />
TRI-TAB ®<br />
A-TAB ®<br />
DI-TAB ®<br />
Equilibrium moisture adsorption isotherm at 25°C expressed as %<br />
water on an anhydrous basis vs. relative humidity. Moisture determined<br />
for A-TAB ® and TRI-TAB ® at 105°C; for DI-TAB ® at 60°C.<br />
While TRI-TAB ® is slightly hygroscopic and may<br />
pick up surface moisture or contain moisture<br />
in small pores, it does not form a well-defined<br />
crystalline hydrate, and surface moisture can be<br />
readily removed in an oven. The moisture content<br />
of TRI-TAB ® can be determined by drying at 105°<br />
and is typically about 0.2%. High temperatures<br />
(>100°C) can also be used to determine the<br />
surface moisture of A-TAB ® , because A-TAB ® is<br />
an anhydrous material. Unlike A-TAB ® , moisture<br />
determination or weight loss-on-drying for DI-TAB ® ,<br />
dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, is done at 60°C.<br />
At higher temperatures, some of the waters of<br />
hydration of DI-TAB ® are removed, leading to<br />
incorrect high surface moisture values.<br />
When DI-TAB ® or powdered dicalcium phosphate<br />
dihydrate is dehydrated, it cannot be rehydrated<br />
again to form the dihydrate. Thus, a formulation<br />
exposed to high temperatures, say 50° or 60°C,<br />
can irreversibly lose water.<br />
The anhydrous dicalcium phosphate salt will not<br />
pick up water to form the dihydrate because it<br />
is a thermodynamically stable material. In a wet<br />
granulation, the anhydrous remains anhydrous<br />
as shown by its X-ray diffraction powder pattern.<br />
Compatibilities and Stability<br />
A well-known incompatibility for calcium salts<br />
is with the tetracycline antibiotics. These drugs<br />
should not be taken within two hours of eating<br />
dairy products such as milk, yogurt or cheese,<br />
or taking calcium or iron supplements.<br />
Hydroxyapatite is incompatible with tocopheryl<br />
acetate (but not with tocopheryl succinate). The<br />
reason is attributed to the large number of hydroxyl<br />
groups on the hydroxyapatite surface and the large<br />
surface area of this excipient.<br />
DI-TAB ® , which contains waters of crystallization,<br />
is stable during storage under normal conditions<br />
(20° – 40°C). However, some of this water can be<br />
lost during storage at higher temperatures and<br />
may interact with water-sensitive ingredients in a<br />
formulation. Accelerated stability testing of tablets<br />
containing DI-TAB ® Should not be done at high<br />
temperatures of 50° – 60°C, as they will yield<br />
erroneous results. This can give rise to some<br />
apparent incompatibilities at higher temperatures,<br />
where the released moisture may interact with<br />
drugs, vitamins and other excipients. To extrapolate<br />
such findings to room temperature would be<br />
erroneous, since dicalcium phosphate dihydrate<br />
does not dehydrate at this temperature.<br />
Arrhenius plots should not be done for dicalcium<br />
phosphate dihydrate dosage forms which have<br />
been stored under high temperature conditions<br />
because the dihydrate may no longer be present.<br />
10