Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
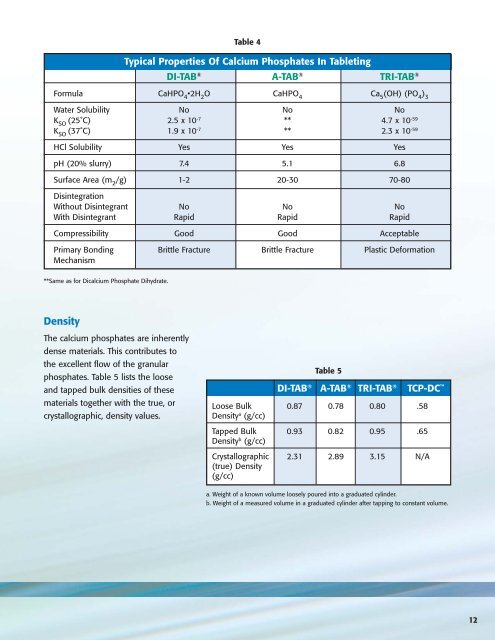
Table 4<br />
Typical Properties Of <strong>Calcium</strong> <strong>Phosphate</strong>s In Tableting<br />
DI-TAB ® A-TAB ® TRI-TAB ®<br />
Formula CaHPO 4<br />
•2H 2<br />
O CaHPO 4<br />
Ca 5<br />
(OH) (PO 4<br />
) 3<br />
Water Solubility No No No<br />
K SO<br />
(25˚C) 2.5 x 10 -7 ** 4.7 x 10 -59<br />
K SO<br />
(37˚C) 1.9 x 10 -7 ** 2.3 x 10 -59<br />
HCl Solubility Yes Yes Yes<br />
pH (20% slurry) 7.4 5.1 6.8<br />
Surface Area (m 2<br />
/g) 1-2 20-30 70-80<br />
Disintegration<br />
Without Disintegrant No No No<br />
With Disintegrant Rapid Rapid Rapid<br />
Compressibility Good Good Acceptable<br />
Primary Bonding Brittle Fracture Brittle Fracture Plastic Deformation<br />
Mechanism<br />
**Same as for Dicalcium <strong>Phosphate</strong> Dihydrate.<br />
Density<br />
The calcium phosphates are inherently<br />
dense materials. This contributes to<br />
the excellent flow of the granular<br />
phosphates. Table 5 lists the loose<br />
and tapped bulk densities of these<br />
materials together with the true, or<br />
crystallographic, density values.<br />
Table 5<br />
DI-TAB ® A-TAB ® TRI-TAB ® TCP-DC <br />
Loose Bulk 0.87 0.78 0.80 .58<br />
Density a (g/cc)<br />
Tapped Bulk 0.93 0.82 0.95 .65<br />
Density b (g/cc)<br />
Crystallographic 2.31 2.89 3.15 N/A<br />
(true) Density<br />
(g/cc)<br />
a. Weight of a known volume loosely poured into a graduated cylinder.<br />
b. Weight of a measured volume in a graduated cylinder after tapping to constant volume.<br />
12