Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Calcium Phosphate Excipients - Innophos
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Figure 21 Figure 22<br />
20<br />
20<br />
Tablet Hardness (kp)<br />
16<br />
12<br />
8<br />
4<br />
0<br />
8<br />
0.5% Mg Stearate<br />
1.0% Mg Stearate<br />
(2.0% Mg Stearate gave no tablets)<br />
10 12 14 16 18 20 22<br />
Compaction Force (kN)<br />
Tablet Hardness (kp)<br />
16<br />
12<br />
8<br />
4<br />
0<br />
8<br />
2-Minute blend<br />
30-minute blend<br />
10 12 14 16 18 20<br />
Compaction Force (kN)<br />
22<br />
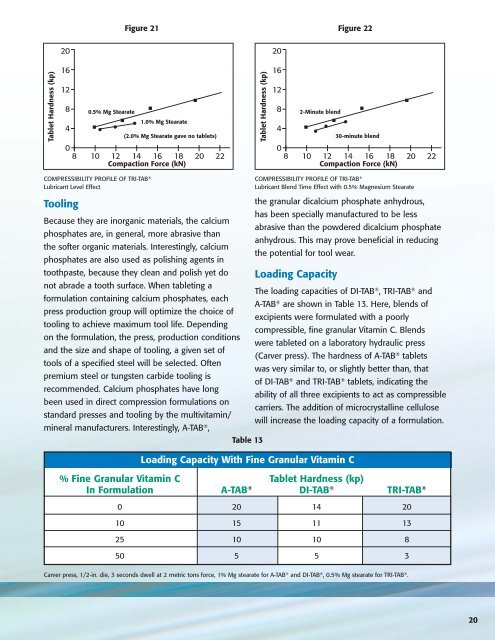
COMPRESSIBILITY PROFILE OF TRI-TAB ®<br />
Lubricant Level Effect<br />
Tooling<br />
Because they are inorganic materials, the calcium<br />
phosphates are, in general, more abrasive than<br />
the softer organic materials. Interestingly, calcium<br />
phosphates are also used as polishing agents in<br />
toothpaste, because they clean and polish yet do<br />
not abrade a tooth surface. When tableting a<br />
formulation containing calcium phosphates, each<br />
press production group will optimize the choice of<br />
tooling to achieve maximum tool life. Depending<br />
on the formulation, the press, production conditions<br />
and the size and shape of tooling, a given set of<br />
tools of a specified steel will be selected. Often<br />
premium steel or tungsten carbide tooling is<br />
recommended. <strong>Calcium</strong> phosphates have long<br />
been used in direct compression formulations on<br />
standard presses and tooling by the multivitamin/<br />
mineral manufacturers. Interestingly, A-TAB ® ,<br />
Table 13<br />
COMPRESSIBILITY PROFILE OF TRI-TAB ®<br />
Lubricant Blend Time Effect with 0.5% Magnesium Stearate<br />
the granular dicalcium phosphate anhydrous,<br />
has been specially manufactured to be less<br />
abrasive than the powdered dicalcium phosphate<br />
anhydrous. This may prove beneficial in reducing<br />
the potential for tool wear.<br />
Loading Capacity<br />
The loading capacities of DI-TAB ® , TRI-TAB ® and<br />
A-TAB ® are shown in Table 13. Here, blends of<br />
excipients were formulated with a poorly<br />
compressible, fine granular Vitamin C. Blends<br />
were tableted on a laboratory hydraulic press<br />
(Carver press). The hardness of A-TAB ® tablets<br />
was very similar to, or slightly better than, that<br />
of DI-TAB ® and TRI-TAB ® tablets, indicating the<br />
ability of all three excipients to act as compressible<br />
carriers. The addition of microcrystalline cellulose<br />
will increase the loading capacity of a formulation.<br />
Loading Capacity With Fine Granular Vitamin C<br />
% Fine Granular Vitamin C Tablet Hardness (kp)<br />
In Formulation A-TAB ® DI-TAB ® TRI-TAB ®<br />
0 20 14 20<br />
10 15 11 13<br />
25 10 10 8<br />
50 5 5 3<br />
Carver press, 1/2-in. die, 3 seconds dwell at 2 metric tons force, 1% Mg stearate for A-TAB ® and DI-TAB ® , 0.5% Mg stearate for TRI-TAB ® .<br />
20