YtDl2r
YtDl2r
YtDl2r
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
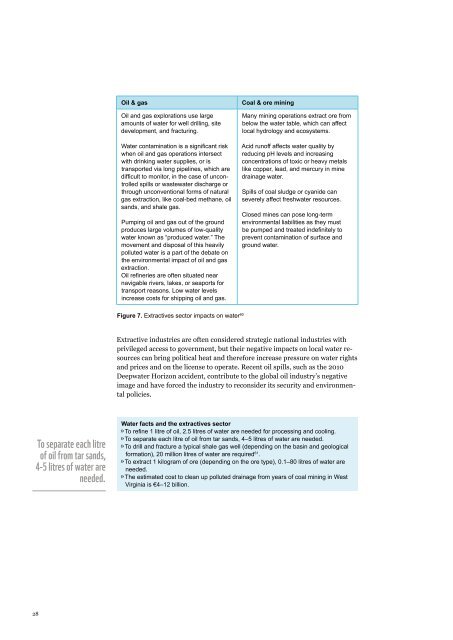
Oil & gas<br />
Oil and gas explorations use large<br />
amounts of water for well drilling, site<br />
development, and fracturing.<br />
Water contamination is a significant risk<br />
when oil and gas operations intersect<br />
with drinking water supplies, or is<br />
transported via long pipelines, which are<br />
difficult to monitor, in the case of uncontrolled<br />
spills or wastewater discharge or<br />
through unconventional forms of natural<br />
gas extraction, like coal-bed methane, oil<br />
sands, and shale gas.<br />
Pumping oil and gas out of the ground<br />
produces large volumes of low-quality<br />
water known as “produced water.” The<br />
movement and disposal of this heavily<br />
polluted water is a part of the debate on<br />
the environmental impact of oil and gas<br />
extraction.<br />
Oil refineries are often situated near<br />
navigable rivers, lakes, or seaports for<br />
transport reasons. Low water levels<br />
increase costs for shipping oil and gas.<br />
Coal & ore mining<br />
Many mining operations extract ore from<br />
below the water table, which can affect<br />
local hydrology and ecosystems.<br />
Acid runoff affects water quality by<br />
reducing pH levels and increasing<br />
concentrations of toxic or heavy metals<br />
like copper, lead, and mercury in mine<br />
drainage water.<br />
Spills of coal sludge or cyanide can<br />
severely affect freshwater resources.<br />
Closed mines can pose long-term<br />
environmental liabilities as they must<br />
be pumped and treated indefinitely to<br />
prevent contamination of surface and<br />
ground water.<br />
Figure 7. Extractives sector impacts on water 60<br />
Extractive industries are often considered strategic national industries with<br />
privileged access to government, but their negative impacts on local water resources<br />
can bring political heat and therefore increase pressure on water rights<br />
and prices and on the license to operate. Recent oil spills, such as the 2010<br />
Deepwater Horizon accident, contribute to the global oil industry’s negative<br />
image and have forced the industry to reconsider its security and environmental<br />
policies.<br />
To separate each litre<br />
of oil from tar sands,<br />
4-5 litres of water are<br />
needed.<br />
Water facts and the extractives sector<br />
»To refine 1 litre of oil, 2.5 litres of water are needed for processing and cooling.<br />
»To separate each litre of oil from tar sands, 4–5 litres of water are needed.<br />
»To » drill and fracture a typical shale gas well (depending on the basin and geological<br />
formation), 20 million litres of water are required 61 .<br />
»To » extract 1 kilogram of ore (depending on the ore type), 0.1–80 litres of water are<br />
needed.<br />
»The » estimated cost to clean up polluted drainage from years of coal mining in West<br />
Virginia is €4–12 billion.<br />
28