'Thin films & coatings' Roadmap - Nano Mahidol
'Thin films & coatings' Roadmap - Nano Mahidol
'Thin films & coatings' Roadmap - Nano Mahidol
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
of organic materials; however, nanotechnology allows retention of these properties,<br />
with regard to transparency mainly because the particles are smaller than the<br />
wavelengths of visible light.<br />
2.2 Most remarkable properties of thin <strong>films</strong><br />
The main advantage of thin <strong>films</strong> (or any other coating) is that materials properties<br />
can be transferred to the surface (thus enabling the use of diverse substrates). The<br />
substrate and the thin film are a material system where each of them provides the<br />
required functionality.<br />
In general, nanotechnology provides the tools for controlling 3 key parameters for<br />
thin <strong>films</strong> performance: chemical composition (and crystalline structure at nano-sized<br />
domains), thickness and topography (including nano-scale patterning of thin <strong>films</strong>’<br />
surface).<br />
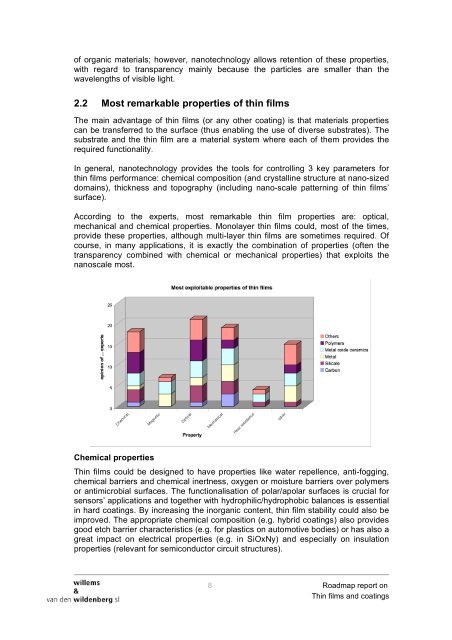
According to the experts, most remarkable thin film properties are: optical,<br />
mechanical and chemical properties. Monolayer thin <strong>films</strong> could, most of the times,<br />
provide these properties, although multi-layer thin <strong>films</strong> are sometimes required. Of<br />
course, in many applications, it is exactly the combination of properties (often the<br />
transparency combined with chemical or mechanical properties) that exploits the<br />
nanoscale most.<br />
Chemical properties<br />
Thin <strong>films</strong> could be designed to have properties like water repellence, anti-fogging,<br />
chemical barriers and chemical inertness, oxygen or moisture barriers over polymers<br />
or antimicrobial surfaces. The functionalisation of polar/apolar surfaces is crucial for<br />
sensors’ applications and together with hydrophilic/hydrophobic balances is essential<br />
in hard coatings. By increasing the inorganic content, thin film stability could also be<br />
improved. The appropriate chemical composition (e.g. hybrid coatings) also provides<br />
good etch barrier characteristics (e.g. for plastics on automotive bodies) or has also a<br />
great impact on electrical properties (e.g. in SiOxNy) and especially on insulation<br />
properties (relevant for semiconductor circuit structures).<br />
8 <strong>Roadmap</strong> report on<br />
Thin <strong>films</strong> and coatings