comparative study for mrr on die-sinking edm using electrode ... - ijater
comparative study for mrr on die-sinking edm using electrode ... - ijater
comparative study for mrr on die-sinking edm using electrode ... - ijater
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Internati<strong>on</strong>al Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering Research (IJATER)<br />
. μsec work piece<br />
(gm)<br />
Tool<br />
(gm)<br />
Wwb Wwa Wtb Wta<br />
1 4 1 50 354.760 354.470 28.923 28.921<br />
2 4 2 50 354.470 353.595 28.921 28.919<br />
3 4 3 50 353.595 352.103 28.919 28.918<br />
4 4 4 50 352.103 350.662 28.918 28.916<br />
5 4 5 50 350.662 349.415 28.916 28.914<br />
D C = Diameter of copper <strong>electrode</strong>,<br />
I = Current,<br />
Wwb = Weight of the workpiece be<str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g>e machining<br />
Wwa = Weight of the workpiece after machining<br />
Wtb = Weight of the tool be<str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g>e machining<br />
Wta = Weight of the tool after machining<br />
N. (mm) (A) (μsec) (mm3/min) (gm/min)<br />
1 4 1 50 0.743 1.67E-05<br />
2 4 2 50 1.942 1.67E-05<br />
3 4 3 50 3.199 1.67E-05<br />
4 4 4 50 3.144 3.33E-05<br />
5 4 5 50 2.800 3.33E-05<br />
Table 5 MMR and TWR <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> Copper <strong>electrode</strong><br />
S.N.<br />
Dc<br />
(mm)<br />
I<br />
(A)<br />
T<strong>on</strong><br />
(μsec)<br />
MRR<br />
(mm3/min)<br />
TWR<br />
(gm/min)<br />
S<br />
N<br />
1 4 1 50 0.616 3.33E-05<br />
2 4 2 50 1.858 3.33E-05<br />
3 4 3 50 3.168 1.67E-05<br />
4 4 4 50 3.059 3.33E-05<br />
5 4 5 50 2.647 3.33E-05<br />
Dg<br />
mm<br />
I<br />
(A)<br />
Table 6 Material removal <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> graphite <strong>electrode</strong><br />
Weight<br />
Weight<br />
Of<br />
Of<br />
T<strong>on</strong> work piece<br />
Tool<br />
μsec (gm)<br />
(gm)<br />
Wwb Wwa Wtb Wta<br />
1 4 1 50 349.415 349.065 19.781 19.780<br />
2 4 2 50 349.065 348.15 19.780 19.779<br />
3 4 3 50 348.15 346.643 19.779 19.778<br />
4 4 4 50 346.643 345.162 19.778 19.776<br />
5 4 5 50 345.162 343.843 19.776 19.774<br />
D g = Diameter of graphite <strong>electrode</strong>,<br />
I = Current,<br />
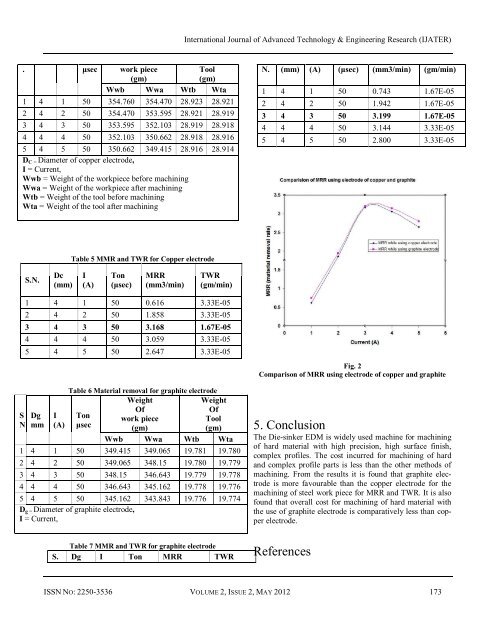
Fig. 2<br />
Comparis<strong>on</strong> of MRR <strong>using</strong> <strong>electrode</strong> of copper and graphite<br />
5. C<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong><br />
The Die-sinker EDM is widely used machine <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> machining<br />
of hard material with high precisi<strong>on</strong>, high surface finish,<br />
complex profiles. The cost incurred <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> machining of hard<br />
and complex profile parts is less than the other methods of<br />
machining. From the results it is found that graphite <strong>electrode</strong><br />
is more favourable than the copper <strong>electrode</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> the<br />
machining of steel work piece <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> MRR and TWR. It is also<br />
found that overall cost <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> machining of hard material with<br />
the use of graphite <strong>electrode</strong> is <str<strong>on</strong>g>comparative</str<strong>on</strong>g>ly less than copper<br />
<strong>electrode</strong>.<br />
Table 7 MMR and TWR <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> graphite <strong>electrode</strong><br />
S. Dg I T<strong>on</strong> MRR TWR<br />
References<br />
ISSN NO: 2250-3536 VOLUME 2, ISSUE 2, MAY 2012 173