2011 Apop.pdf - Lab-JOT
2011 Apop.pdf - Lab-JOT
2011 Apop.pdf - Lab-JOT
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Signaling Pathways<br />
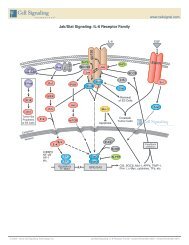
Death Receptor Signaling<br />
MKK7<br />
JNK<br />
Bcl-2<br />
ASK1<br />
FasL<br />
Fas/<br />
CD95<br />
Daxx<br />
Pro-<strong>Apop</strong>totic<br />
Pro-Survival<br />
Caspase-8,-10<br />
RIP<br />
Bcl-2<br />
FADD<br />
Bid<br />
tBid<br />
Caspase-6<br />
DAPK<br />
FADD<br />
Cyto c<br />
Death Receptor Signaling<br />
TNF-α<br />
TNFR-1 TNFR-2 DR3<br />
APO-3<br />
TRADD<br />
Apaf-1<br />
FLIP<br />
TRADD<br />
RIP CYLD<br />
RAIDD<br />
ASK1<br />
Caspase-9<br />
TRAF2<br />
HtrA2<br />
Smac<br />
ub<br />
Lamin A Actin Gas2 Fodrin Rock-1 ICAD Acinus<br />
PARP<br />
c-IAP1/2<br />
NIK<br />
IKK<br />
IκB<br />
ub<br />
NF-κB<br />
NF-κB<br />
XIAP<br />
TNF-α<br />
Caspase-3<br />
CAD<br />
TRAF2<br />
FLIPs<br />
TRAF2<br />
RIP<br />
TRADD<br />
APO-3L/<br />
TWEAK<br />
+zVAD<br />
TRADD<br />
FADD<br />
Caspase-8,-10<br />
Caspase-7<br />
DNA Repair<br />
Cell Shrinkage<br />
Membrane Blebbing DNA Fragmentation Chromatin Condensation<br />
<strong>Apop</strong>tosis<br />
www.cellsignal.com<br />
FADD<br />
© 2003–<strong>2011</strong> Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.<br />
APO-2L/<br />
TRAIL<br />
DR4/5<br />
ComplexIIb<br />
RIP1<br />
RIP3<br />
Necroptosis<br />
Pathway Description: <strong>Apop</strong>tosis can be induced through the activation of death receptors including Fas, may also activate JNK via ASK1/MKK7. Activation of JNK may lead to the inhibition of Bcl-2 by phosphorylation.<br />
TNFαR, DR3, DR4, and DR5 by their respective ligands. Death receptor ligands characteristically initiate<br />
In the absence of caspase activation, stimulation of death receptors can lead to the activation of an<br />
signaling via receptor oligomerization, which in turn results in the recruitment of specialized adaptor proteins<br />
alternative programmed cell death pathway termed necroptosis by forming complex IIb.<br />
and activation of caspase cascades. Binding of FasL induces Fas trimerization, which recruits initiator<br />
Selected Reviews:<br />
caspase-8 via the adaptor protein FADD. Caspase-8 then oligomerizes and is activated via autocatalysis.<br />
Declercq, W. et al. (2009) RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and survival. Cell 138, 229–232.<br />
Activated caspase-8 stimulates apoptosis via two parallel cascades: it can directly cleave and activate<br />
Humphreys, R.C. and Halpern, W. (2008) Trail receptors: targets for cancer therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.<br />
caspase-3, or alternatively, it can cleave Bid, a pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family protein. Truncated Bid (tBid)<br />
615, 127–158.<br />
translocates to mitochondria, inducing cytochrome c release, which sequentially activates caspase-9 and<br />
Logue, S.E. and Martin, S.J. (2008) Caspase activation cascades in apoptosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans.<br />
-3. TNF-α and DR-3L © 2002 can – deliver 2010 pro- Cell Signaling or anti-apoptotic Technology, signals. Inc. TNFαR and DR3 promote apoptosis via<br />
Death Receptor Signaling • created January 2002 • revised November 2010<br />
36, 1–9.<br />
the adaptor proteins TRADD/FADD and the activation of caspase-8. Interaction of TNF-α with TNFαR may<br />
Van Herreweghe, F. et al. (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst,<br />
activate the NF-κB pathway via NIK/IKK. The activation of NF-κB induces the expression of pro-survival<br />
that’s the question. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1567–1579.<br />
genes including Bcl-2 and FLIP, the latter can directly inhibit the activation of caspase-8. FasL and TNF-α<br />
Zakeri, Z. and Lockshin, R.A. (2008) Cell death: history and future. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 615, 1–11.<br />
Survival Factors:<br />
Growth Factors, Cytokines, etc.<br />
PKA<br />
14-3-3<br />
Bcl-2 Family<br />
PKC<br />
Pro-<strong>Apop</strong>totic<br />
Pro-Survival<br />
Erk1/2<br />
p90RSK<br />
Bad<br />
14-3-3<br />
Bad<br />
Cytosolic<br />
Sequestration<br />
HSP60<br />
PI3K<br />
Akt<br />
Caspase-3<br />
p70 S6K<br />
Calcineurin<br />
Apaf-1<br />
Caspase-9<br />
ub<br />
Mitochondrial Control of <strong>Apop</strong>tosis<br />
Mitochondrial Control of <strong>Apop</strong>tosis<br />
XIAP<br />
Caspase-8,-10<br />
Arts<br />
FADD<br />
Bid<br />
FasL<br />
Fas/<br />
CD95<br />
tBid<br />
Bax<br />
Bax<br />
Bad<br />
Cyto c<br />
Mule<br />
Bak<br />
Bak<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
HtrA2<br />
<strong>Apop</strong>tosis<br />
Mcl-1<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
tBid<br />
Smac/<br />
Diablo<br />
Mcl-1<br />
Bim<br />
LC8<br />
Microtubules<br />
LC8<br />
Bmt<br />
Puma<br />
AIF<br />
Bim<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Mule<br />
Endo G<br />
Hrk<br />
DP5<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Bmt<br />
Hrk<br />
DP5<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Noxa<br />
Death Stimuli:<br />
Survival Factor Withdrawal<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Bax<br />
Bax<br />
p53<br />
ATM/<br />
ATR<br />
JNK<br />
DNA Damage<br />
Genotoxic Stress<br />
ING2<br />
[NAD]<br />
SirT2<br />
www.cellsignal.com<br />
JNK<br />
Bax<br />
Caspase-2<br />
Pathway Description: The Bcl-2 family of proteins regulate apoptosis by controlling mitochondrial<br />
channel (VDAC), which may play a role in regulating cytochrome c release. Mule/ARF-BP1 is a DNA damage<br />
activated E3 ubiquitin ligase for p53, and Mcl-1, an anti-apoptotic member of Bcl-2.<br />
permeability. The anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL reside in the outer mitochondrial wall and inhibit<br />
cytochrome c release. The proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins Bad, Bid, Bax, and Bim may reside in the cytosol but<br />
Selected Reviews:<br />
translocate to mitochondria following death signaling, where they promote the release of cytochrome c. Bad<br />
Brenner, D. and Mak, T.W. (2009) Mitochondrial cell death effectors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 21, 871–877.<br />
translocates to mitochondria and forms a pro-apoptotic complex with Bcl-xL. This translocation is inhibited<br />
Chalah, A. and Khosravi-Far, R. (2008) The mitochondrial death pathway. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 615, 25–45.<br />
by survival factors that induce the phosphorylation of Bad, leading to its cytosolic sequestration. Cytosolic<br />
Pradelli, L.A. et al. (2010) Mitochondrial control of caspase-dependent and -independent cell death.<br />
Bid is cleaved by caspase-8 following signaling through Fas; its active fragment (tBid) translocates to mitochondria.<br />
Bax and Bim © 2003 translocate – 2010 Cell to mitochondria Signaling Technology, in response Inc. to death stimuli, including survival factor Mitochondrial Control of <strong>Apop</strong>tosis • created February 2003 • revised November 2010<br />
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1589–1597.<br />
Rong, Y. and Distelhorst, C.W. (2008) Bcl-2 protein family members: versatile regulators of calcium<br />
withdrawal. Activated following DNA damage, p53 induces the transcription of Bax, Noxa, and PUMA. Upon<br />
signaling in cell survival and apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 70, 73–91.<br />
release from mitochondria, cytochrome c binds to Apaf-1 and forms an activation complex with caspase-9.<br />
Speidel D. (2010) Transcription-independent p53 apoptosis: an alternative route to death. Trends Cell Biol.<br />
Although the mechanism(s) regulating mitochondrial permeability and the release of cytochrome c during<br />
20, 14–24.<br />
apoptosis are not fully understood, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bax may influence the voltage-dependent anion<br />
Suen, D.F. et al. (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 22, 1577–1590.<br />
CaMKII<br />
RAIDD<br />
PIDD<br />
© 2002–<strong>2011</strong> Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.<br />
22<br />
Direct Stimulatory Modification<br />
Direct Inhibitory Modification<br />
Multistep Stimulatory Modification<br />
Multistep Inhibitory Modification<br />
Tentative Stimulatory Modification<br />
Tentative Inhibitory Modification<br />
Transcriptional Stimulatory Modification<br />
Separation of Subunits or Cleavage Products<br />
Kinase<br />
Transcription Factor<br />
Receptor<br />
Pro-apoptotic<br />
Transcriptional Inhibitory Modification Joining of Subunits<br />
Translocation<br />
Phosphatase<br />
Caspase Enzyme Anti-apoptotic<br />
GAP<br />
GEF<br />
GTPase<br />
G-protein, ribosomal subunit<br />
23