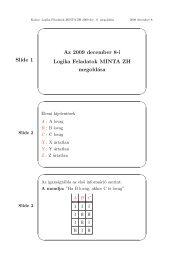
Slide 1 First-order Logic
Slide 1 First-order Logic
Slide 1 First-order Logic
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Kabos: Intro<strong>Logic</strong> <strong>First</strong>-<strong>order</strong> theories / 2<br />
Semantics<br />
Interpretation of a formula: substituting values into variables.<br />
A variable takes an element from the universe, and the interpreted formula<br />
takes either T or F<br />
Model of S : an interpretation when all formulae in S are T<br />
S |= ϕ means that ϕ is entailed by S, that is ϕ takes T in every possible<br />
model of S<br />
Soundness: if S ⊢ ϕ then S |= ϕ<br />
Completeness: if S |= ϕ then S ⊢ ϕ<br />
It can be seen, that Propositional <strong>Logic</strong> is sound and complete.<br />
<strong>First</strong>-<strong>order</strong> Calculus<br />
Individual variable: (in <strong>First</strong>-<strong>order</strong> Calculus)<br />
an element of a given Universe set U.<br />
List of symbols:<br />
1. individual variables: x, y, z , ...<br />
2. constants: c,...<br />
3. predicate variables (relations): P, Q, R ...<br />
4. functions: f, g<br />
5. quantifiers, universal: ∀ , existential: ∃<br />
6. logical operators: ¬, &, ∨, →, ↔, ...<br />
7. parentheses ( left , right)<br />
Term: is defined recursively by the rules<br />
1. individual variables and constants are terms,<br />
2. if t 1 , .., t N are terms and f is a function then f(t 1 , t 2 , ..., t N ) is a term,<br />
3. nothing else is a term.<br />
Atomic formula:<br />
If P is a predicate variable andt 1 , t 2 , ..., t N are terms, then P (t 1 , t 2 , ..., t N )<br />
is an atomic formula