M2110 Hardware Reference Manual - MEMSIC
M2110 Hardware Reference Manual - MEMSIC
M2110 Hardware Reference Manual - MEMSIC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
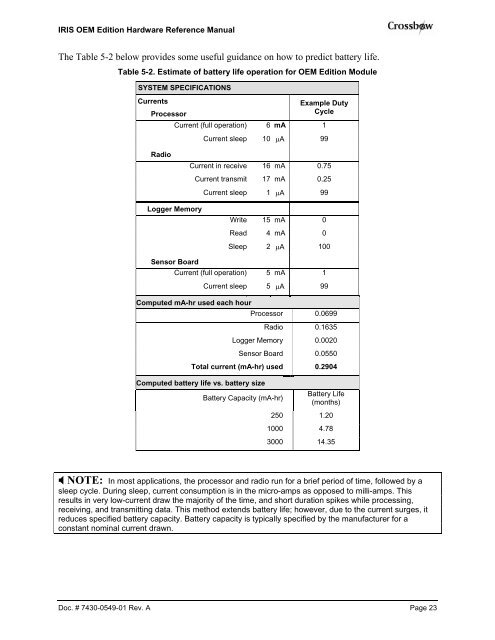
IRIS OEM Edition <strong>Hardware</strong> <strong>Reference</strong> <strong>Manual</strong>The Table 5-2 below provides some useful guidance on how to predict battery life.Table 5-2. Estimate of battery life operation for OEM Edition ModuleSYSTEM SPECIFICATIONSCurrentsProcessorExample DutyCycleCurrent (full operation) 6 mA 1Current sleep 10 µA 99RadioCurrent in receive 16 mA 0.75Current transmit 17 mA 0.25Current sleep 1 µA 99Logger MemoryWrite 15 mA 0Read 4 mA 0Sleep 2 µA 100Sensor BoardCurrent (full operation) 5 mA 1Current sleep 5 µA 99Computed mA-hr used each hourProcessor 0.0699Radio 0.1635Logger Memory 0.0020Sensor Board 0.0550Total current (mA-hr) used 0.2904Computed battery life vs. battery sizeBattery Capacity (mA-hr)Battery Life(months)250 1.201000 4.783000 14.35 NOTE: In most applications, the processor and radio run for a brief period of time, followed by asleep cycle. During sleep, current consumption is in the micro-amps as opposed to milli-amps. Thisresults in very low-current draw the majority of the time, and short duration spikes while processing,receiving, and transmitting data. This method extends battery life; however, due to the current surges, itreduces specified battery capacity. Battery capacity is typically specified by the manufacturer for aconstant nominal current drawn.Doc. # 7430-0549-01 Rev. A Page 23