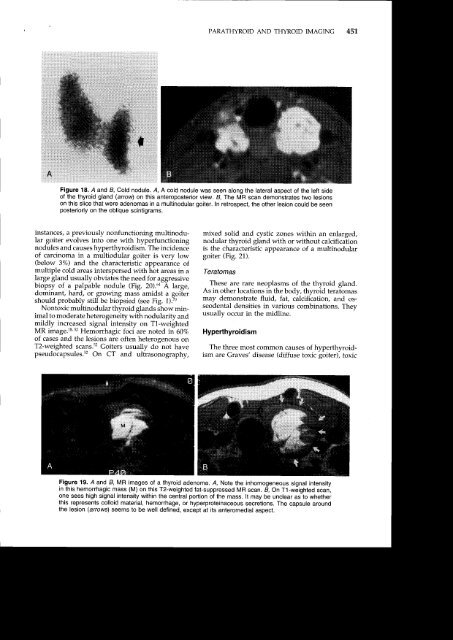
450 YOUSEMFigure 16. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the thyroidgland. The multiple masses in this enlarged thyroid glandwere caused by metastases from a primary renal cell carcinoma.Because the thyroid gland absorbs so much iodinateddye, they appear as filling defects amidst the gland.nodules include thyroiditis, normal variation in thyroidfunction, and ectopic tissue.58"Toxic" adenomas rarely cause clinically apparenthyperthyroidism until they exceed 2.5 cm insize.16 The patient usually presents with a slowlygrowing neck mass. The imaging features of toxicadenomas are nonspecific on nonscintigraphic modalities.The lesions are usually solid and enhancing.N onfu nction i ng Thy roi d Ade n omasA cold (nonfunctioning) nodule is approachedmore aggressively than a hot nodule because ofthe higher rate of malignancy, especially in youngwomen and in men of all ages. A biopsy or aspirationis often required early in the diagnostic algo-rithm. The majority of cold nodules are caused bydegenerated (follicular) adenomas (Fig. 18) nodularhemorrhage, cysts, goiters, inflammatory conditions(see subsequent discussion), or amyloid deposition.6aFollicular adenomas occur in all age groups,in women more than in men, and are usually lessthan 3 cm in size. As adenomas outgrow their bloodsupply, they may involute or encyst. Alternatively,they may develop intralesional hemorrhage (andacutely expand), necrosis, calcification, or scarring.Malignant degeneration is not believed to occurin adenomas.Hurthle's cell adenomas (which some investiqatorsbelieve are malignant in character) are morevariable in size and shape with less well-definedborders.Occasionallp one will find a hyperplastic adenomathat is responsive to TSH in a patient withGrave's disease. this appea.s as a cold nodule becausethe hyperthyroidism of Grave's disease suppressesTSH, which in turn suppresses the adenomaon a nuclear medicine studv. This entitv is calledMa r i n e- Le nha r t sy nd ro me.oaIn one of the earliest articles on the subiect of MRimaging, Gefter and colleagues identified adenomatousnodules as small as 4 mm to 5 mm in size.l8They noted that follicular adenomas appeared aswell-circumscribed nodules with heterogeneous intensity,bright on T2-weighted images (Fig. 19).CystsMost thyroid cysts actually represent degenerationof adenomas. Cysts of any kind are anechoicor echopenic on ultrasonography, show a distinctback wall, and demonstrate enhanced throughtransmission.They are low density on CT unlesshemorrhagic or infected. The density and intensityof the cyst mav not simulate that of cerebrospinalfluid on CT anci trrtR imaging because of the p.esen"eof hyperproteinaceous colloid within the cyst. Col-Ioid cysts are characterizedby homogeneous highsignalon Tl-weighted scans6a; however, this findingis not specific to colloid cysts because areas of hemorrhage,also bright on Tl-weighted scans, can beseen in goiters, adenomas, and traumatized cysts.Even thyroglossal duct cysts (vide infra) may behyperintense because of high protein content.Figure 17. Hot nodule on nuclear scintigraphy. Note intenseupdate of radiotracer in this functioning adenoma(arrow). The remainder of the gland shows relatively littleuptake owing to the suppression incurred by reduced TSHfrom the outpouring of thyroid hormone by the "toxicnodule."Multinodular GoiterAnother common palpable thyroid abnormalityis the multinodular goiter. A goiter is simply anenlarged thyroid gland that may be seen with hyperthyroidismor hypothyroidism. In the UnitedStates, the common vernacular is to imply a nontoxicgoiter when the term is used. A euthyroidor hypothyroid goiter is the most common thyroidlesion in the United States. Patients, usually olderwomen, present because of hypothyroidism, neckmasses, or tracheal-esophageal compression. In rare
<strong>PARA<strong>THYROID</strong></strong> <strong>AND</strong> <strong>THYROID</strong> <strong>IMAGING</strong>45'],Figure 18. A and B, Cold nodule. A, A cold nodule was seen along the lateral aspect of the left sideof the thyroid gland (arrow) on this anteroposterior view. B, The MR scan demonstrates two lesionson this slice that were adenomas in a multinodular goiter. In retrospect, the other lesion could be seenposteriorly on the oblique scintigrams.instances, a previously nonfunctioning multinodulargoiter evolves into one with hyperfunctioningnodules and causes hyperthyroidism. The incidenceof carcinoma in a multiodular goiter is very low(below 3%) and the characteristic appearance ofmultiple cold areas interspersed with hot areas in alarge gland usually obviates the need for aggressivebiopsy of a palpable nodule (Fig. 20).6a A large,dominant, hard, or growing mass amidst a goitershould probably still be biopsied (see Fig. 1).70Nontoxic multinodular thyroid glands show minimalto moderate heterogeneity with nodularity andmildly increased signal intensity on T1-weightedMR image.l& s2 Hemorrhagic foci are noted in 60%of cases and the lesions are often heterogenous onT2-weighted scans.s2 Goiters usually dJnot havepseudocapsules.s2 On CT and ultrasonography,mixed solid and cystic zones within an enlarged,nodular thyroid gland with or without calcificationis the characteristic appearance of a multinodulargoiter (Fig. 21).TeratomasThese are rare neoplasms of the thyroid gland.As in other locations in the body, thyroid teratomasmay demonstrate fluid, fat, c;lcificatiory and osseodentaldensities in various combinations. Theyusually occur in the midline.HyperthyroidismThe three most common causes of hyperthyroidismare Graves' disease (diffuse toxic goiter), toxicFigure 19. A and B, MR images of a thyroid adenoma. A, Note the inhomogeneousignal intensityin this hemorrhagic mass (M) on this T2-weighted fat-suppressed MR scan. B, On T1-weighted scan,one sees high signal intensity within the central portion of the mass. lt may be unclear as to whetherthis represents colloid material, hemorrhage, or hyperproteinaceous secretions. The capsule aroundthe lesion (arrows) seems to be well defined, except at its anteromedial aspect.