LC/MS/MS Analysis of Gabapentin, Benzodiazepines, and Opiates
LC/MS/MS Analysis of Gabapentin, Benzodiazepines, and Opiates
LC/MS/MS Analysis of Gabapentin, Benzodiazepines, and Opiates
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
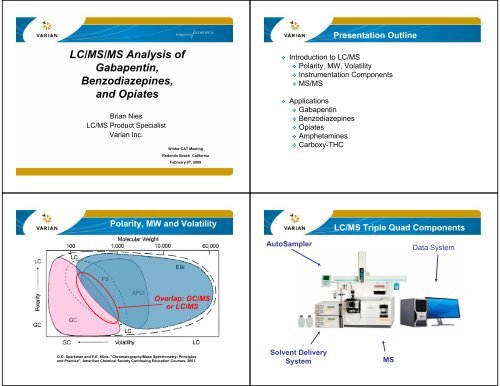
Presentation Outline<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong><strong>Gabapentin</strong>,<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> <strong>Benzodiazepines</strong>,Introduction <strong>and</strong>Applications<strong>and</strong> <strong>Opiates</strong>Brian Nies<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> Product SpecialistVarian Inc.Winter CAT MeetingRedondo Beach CaliforniaFebruary 6 th , 2008 Introduction to <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> Polarity, MW, Volatility Instrumentation Components <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> Applications <strong>Gabapentin</strong> <strong>Benzodiazepines</strong> <strong>Opiates</strong> Amphetamines Carboxy-THCPolarity, MW <strong>and</strong> Volatility<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> Triple Quad ComponentsAutoSamplerData SystemOverlap: GC/<strong>MS</strong>or <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>O.D. Sparkman <strong>and</strong> F.E. Klink, "Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry: Principles<strong>and</strong> Practice", American Chemical Society Continuing Education Courses, 2001.Solvent DeliverySystem<strong>MS</strong>
IonizationSourceDetector<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> AnalyzerQ1Mass AnalyzerVacuum SystemQ3Mass AnalyzerQ2Collision Ce<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> what’s that? <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> is when you have more than one step <strong>of</strong>mass filtration/separation <strong>and</strong> an additional step<strong>of</strong> fragmentation. <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> is used to give an additional level <strong>of</strong>confirmation to an analysis or when very specificresults are required. <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> can also help determine the molecularstructure <strong>of</strong> a molecule.Q2- CurvedCollision CellTriple Quad SRMVarian <strong>MS</strong> Quad: Strong PointsUnique Curved (180°) Collision CellQ1MRM or SRMIonSourceQ1Q3First transitionQ1Q2- CurvedCollision CellExample with a second transition (different precursor <strong>and</strong> fragment ions)Q3Q2Q1Q2- CurvedCollision CellQ3IonsMRM - <strong>of</strong>ten used to describe “Multiple” Reaction Monitoring.SRM – preferred term. Selected Reaction Monitoring (not single).Relating to data acquired from specific product ions correspondingto m/z selected precursor ions.(IUPAC recommendations, www.msterms.com).DetectorQ3
<strong>MS</strong><strong>MS</strong> Using a Curved Collision CellIonSourceQ1• Increased S/N− removal <strong>of</strong> photons, metastable ions& high energy charged droplets fromion detectorQ2NeutralNoise notdeflectedWhy <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>Why <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> for <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>?for <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>?IonsDetectorQ3Limitation <strong>of</strong> API Interfaces Atmospheric Pressure Ionization (API) dominate <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> Electrospray (ES, ESI, APESI) Chemical Ionization (APCI) Photoionization (APPI) All API mechanisms are “s<strong>of</strong>t” Minimal fragment ions formed during ionizationTypically only molecular ion informationPseudo- or quasi-molecular ion(s) Minimal qualitative information for confirmationAdduct ions (Na, K, etc) are not useful forconfirmation1005077109141195EI Full Scan <strong>MS</strong> <strong>of</strong> ReserpineEI-GC/<strong>MS</strong> produces a wide range <strong>of</strong> ions“Information Rich”212226251265301359 381040 90 140 190 240 290 340 390 440 490 540 590(mainlib) Reserpine395HNOONO413 448608Electron Ionization spectrum from NIST; probe sample introductionOOOOOO
ESI (+) Full Scan <strong>MS</strong> <strong>of</strong> ReserpineESI (+) <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> <strong>of</strong> ReserpineAPI-<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> creates very few ionsLimited information(M+H) +After <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> dissociationMore ions = more informationNaadductProduct Ion Scan SpectrumAdvantages <strong>of</strong> <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong><strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> <strong>of</strong>fers increased selectivity for dirtysamples. It helps the users look for smallamounts <strong>of</strong> sample that would otherwise behidden by all the background noise.ApplicationsSame Molecule, <strong>MS</strong> Vs. <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong><strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> capabilities cost more due to additional hardware <strong>and</strong> s<strong>of</strong>twarerequirements in a transmission quadrupole, but <strong>of</strong>ten times theperformance is worth the price increase.
<strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Gabapentin</strong> by<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>What is <strong>Gabapentin</strong>?<strong>Gabapentin</strong>, an analog <strong>of</strong> the neurotransmitter GABA, is usedas an anticonvulsant in the treatment <strong>of</strong> epilepsy.It was approved by the FDA as an anti-seizure medication buthas many controversial <strong>of</strong>f-label uses, such as in the treatment<strong>of</strong> bipolar disorder, social anxiety disorder, obsessivecompulsivedisorder <strong>and</strong> insomnia.<strong>Gabapentin</strong> is also widely used as a pain reliever <strong>and</strong> was one<strong>of</strong> the 50 most prescribed drugs in the United States in 2003due to its mild side-effect pr<strong>of</strong>ile.<strong>Gabapentin</strong> may increase the effect <strong>of</strong> other drugs such asantidepressants, alcohol <strong>and</strong> pain relievers.<strong>Gabapentin</strong> Structure<strong>Gabapentin</strong> Extraction MethodologyChemical structure <strong>of</strong> <strong>Gabapentin</strong>,(1-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexaneacetic acid)Methodology:The extraction <strong>of</strong> <strong>Gabapentin</strong> frombiological specimens is performedusing the principles <strong>of</strong> proteinprecipitation by acetonitrile (withouta clean up step) <strong>and</strong> detection by<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>.Drugs to be determinedby this method:<strong>Gabapentin</strong>, Bacl<strong>of</strong>en (IS),Carbinoxamine (Alternate IS)Instrumentation:Liquid Chromatograph withT<strong>and</strong>em Mass Spectrometer-MassSpectrometer DetectorColumn: Varian Pursuit Diphenyl(DP) Column Dimensions: 3um,50mm x 2.0mm Procedure:Accurately measure 1.0 ml <strong>of</strong>st<strong>and</strong>ard, quality control <strong>and</strong> casesamples.Add 10 ul <strong>of</strong> internal st<strong>and</strong>ard (finalconcentration = 10 ug/ml) to eachtube <strong>and</strong> vortex.Aliquot 50 ul <strong>of</strong> each st<strong>and</strong>ard,quality control <strong>and</strong> case sampleinto new tubes.Add 400 ul <strong>of</strong> acetonitrile to eachtube <strong>and</strong> vortex.Centrifuge for 10 minutes.Decant supernatant to a cleantube. Evaporate the supernatant todryness. Reconstitute the samples with 200ul <strong>of</strong> Methanol: Water (60:40).Vortex.Transfer the liquid to labeledAutoSampler vials with inserts.
Conditions <strong>MS</strong> Conditions:Ionisation Mode: ESI positiveScan Time: 1.0 sDrying Gas: 350 ˚C at 25 psiCollision Cell Pressure: 2.0 mTorrCapillaryVoltage PrecursorProductIonsCollisionEnergyCompounds (V) Ion (m/z) (m/z) (V)<strong>Gabapentin</strong> 65 172 154 -26.50<strong>Gabapentin</strong> 65 172 137 -29.00Bacl<strong>of</strong>en(IS) 65 214 151 -36.50<strong>Gabapentin</strong> <strong>MS</strong> Parameters HP<strong>LC</strong> Conditions: Column: Pursuit Diphenyl 50mm x2.0mm 3u Guard Column: Pursuit Diphenyl2.0mm I.D., 3u Solvent A: Water Solvent B: Methanol Flow Rate: 200µL/min Injection Volume: 25µL <strong>LC</strong> Program:%ATime (min)%B 0:00 60 40 1:001:306054095 3:30 5 95 3:35 60 40 5:00 60 40kCounts 1.0 ug ml std.xms172.0>137.01.0 ug ml std.xms500 172.0>154.040030020010001.0 ug/ml extracted <strong>Gabapentin</strong> (left); Bacl<strong>of</strong>en – IS(right)0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5minutesMCounts1.000.750.500.250.00BACLOFEN (IS) 1.0 ug mlstd.xms 151.0(214.0>151.0)0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5minutes<strong>Gabapentin</strong> Calibration Curve (1.0 ug/ml – 25 ug/ml)<strong>Gabapentin</strong> ConclusionG A B A P E N T I NC u r v e F i t : L i n e a r , O r i g i n : F o r c e , W e i g h t : N o n e R e s p . F a c t . R S D : 6 . 9y = + 1 . 0 7 0 8 0 6 xC o e f f . D e t . ( r 2 ) : 0 . 9R e p l i c a t e s1 1 1 1 1 12 . 52 . 01 . 51 . 0Peak Size / PS Std.0 . 5<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> is utilized in the analysis <strong>of</strong> gabapentin because itallows for a simple, cost-effective clean up, requires noderivatization <strong>of</strong> the drug <strong>and</strong> provides accurate results withexcellent sensitivity.This application demonstrates that the Varian triple quadrupole<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> can identify <strong>and</strong> quantify <strong>Gabapentin</strong> in postmortemspecimens with the use <strong>of</strong> two MRM transitions.Varian Inc. would like to provide a special thank you to SaraKegler <strong>and</strong> Dan Anderson from Los Angeles County Department<strong>of</strong> Coroner for the validation <strong>of</strong> both the extraction procedure<strong>and</strong> the instrument parameters.0 . 00 . 5 1 . 0 1 . 5 2 . 0 2 . 5A m t / M L A m o u n t / . S t d . ( U G )RSD = 6.9%; r2 = 0.999
Introduction to <strong>Benzodiazepines</strong><strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Benzodiazepines</strong>by<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> <strong>Benzodiazepines</strong> are central nervous systemdepressants. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium®)was discovered in 1954 by the Austrian scientist. In 1963 approval for use was given to diazepam(Valium®) - a simplified version <strong>of</strong> Librium - primarily tocounteract anxiety symptoms. Currently, fifteen members <strong>of</strong> this group are marketed inthe United States, <strong>and</strong> about 20 additionalbenzodiazepines are marketed in other countries.Benzodiazepine Experimental ConditionsCapillary Q1 Q3 Collision AnalyteCID Energy Triple Quadrupole <strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> ESI Positive <strong>LC</strong> Conditions: Column: Varian C18 Taxsil 100X2mm,3u Flow Rate: 0.3 mL/min A: 5mM Ammonium Formate B: ACN Time (min) %A %B 0:00 70 30 0:30 70 3010:00 50 5010:30 70 30 15:00 70 30 Injection Volume, 10 uL Mass Spec conditions: ESI Positive Mode Argon pressure: 2.0 mtorr Q1/Q3 peak width: 1.0/1.0amu Samples Protein PrecipitationExtraction Method Complex Matrix Reconstituted in 50:50MeOH:WaterBenzodiazepineMass SpecDetails+ 73.0Volts 271.0 140.0 -24.0Volts Nordiazepam+ 73.0Volts 271.0 165.0 -24.0Volts+ 70.0Volts 285.0 193.0 -24.0Volts Diazepam+ 70.0Volts 285.0 154.0 -19.5Volts+ 70.0Volts 286.0 222.0 -18.5Volts 7-Aminoclonazepam+ 70.0Volts 286.0 121.0 -23.0Volts+ 61.0Volts 287.0 241.0 -10.5Volts Oxazepam+ 61.0Volts 287.0 269.0 -12.0Volts+ 69.0Volts 290.0 226.0 -18.5Volts D-4 7-Aminoclonazepam+ 69.0Volts 290.0 121.0 -23.0Volts+ 69.0Volts 290.1 198.0 -24.0Volts D-5 Diazepam+ 69.0Volts 290.1 154.0 -19.5Volts+ 72.0Volts 292.0 246.0 -10.5Volts D-5 Oxazepam+ 72.0Volts 292.0 274.0 -12.0Volts+ 60.0Volts 301.0 255.0 -18.5Volts Temazepam+ 60.0Volts 301.0 283.0 -10.5Volts+ 80.0Volts 309.0 281.0 -23.5Volts Alprazolam+ 80.0Volts 309.0 205.0 -36.5Volts+ 85.0Volts 314.1 286.0 -18.5Volts D-5 Alprazolam+ 85.0Volts 314.1 268.0 -22.0Volts+ 84.0Volts 316.0 270.0 -20.5Volts Clonazepam+ 84.0Volts 316.0 214.0 -36.0Volts+ 57.0Volts 321.0 275.0 -18.0Volts Lorazepam+ 57.0Volts 321.0 303.0 -16.0Volts
Representative Calibration Curves (10-1000ng/mL)Chromatogram<strong>of</strong> Benzo Mix,250 ng/m<strong>LC</strong>alibratorMCounts271.0>140.0 [-24.0V]100MCounts285.0>193.0 [-24.0V]500MCounts286.0>222.0 [-18.5V]500MCounts287.0>241.0 [-10.5V]0.0MCounts290.0>226.0 [-18.5V]20MCounts290.1>198.0 [-24.0V]200MCounts292.0>246.0 [-10.5V]40MCounts301.0>255.0 [-18.5V]200MCounts309.0>281.0 [-23.5V]400MCounts314.1>286.0 [-18.5V]0MCounts316.0>270.0 [-20.5V]40MCounts321.0>275.0 [-18.0V]4NordiazepamDiazepam7-AminoclonazepamOxazepamD-4 7-AminoclonazepamD-5 DiazepamD-5 OxazepamTemazepamAlprazolamD-5 AlprazolamClonazepamLorazepam7-AminoclonazepamWeight: None Curve Fit: Linear, Origin: Include, Resp. Fact. RSD: 8.179%y = +1.058993x -0.006779Coeff. Det.(r2): 0.9993Replicates32 2 2 2 2 25432Peak Size / PS Std.101 2 3 4 5Amount / Amt. Std. (ng/mL)ClonazepamInclude, Weight: None Curve Fit: Linear, Origin: Resp. Fact. RSD: 5.639%y = +1.054153x +0.013111Coeff. Det.(r2): 0.9978Replicates32 2 2 2 2 25432Peak Size / PS Std.1R(2) = 0.999RSD = 8.17R(2) = 0.997RSD = 5.6402.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 minutesSeg 1, Time: 0.05-15.10, Scan Functions: 282031 4107 6182 8257 10333 Scans01 2 3 4 5Amount / Amt. Std. (ng/mL)Submitted Samples Extracted from Plasma matrixAlternative Benzodiazepine <strong>and</strong> Method <strong>Opiates</strong>UsingUsing the the 320<strong>MS</strong> Vial 01 Opiate Calibrator (500ng/mL) Codeine Hydrocodone Hydromorphone Morphine Oxycodone Vail 02 Unknown Vial 03 Opiate Internal Stds. (2500ng/mL) Codeine D3 Hydrocodone D6 Hydromorphone D6 Morphine D3 Oxycodone D6 Vial 4 Benzo Internal Stds. (250ng/mL) Nordiazepam D5 Alprazolam D5 Hydroxyalprazolam D5 Vial 5 Benzo Calibrator (250 ng/mL) Nordiazepam D5 Alprazolam D5 Hydroxyalprazolam Nordiazepam Alprazolam Hydroxyalprazolam D5 Flurazepam Oxyazepam Lorazepam Clonazepam Desalkylflurazepam Temazepam Diazepam Vials 6 <strong>and</strong> 7 Unknowns
320-<strong>MS</strong> <strong>LC</strong> SystemsBreakdown CurvesHydroxyalprazolamHydrocodone320-<strong>MS</strong>212-<strong>LC</strong>ProStar 430320-<strong>MS</strong>212-<strong>LC</strong>HTS PAL<strong>Benzodiazepines</strong> MethodBenzo Three Ion Monitoring Mobile Phase: 0.1% Formicaq/MeOH Nebulizer Gas: N 2 @ 30psi Drying gas: N 2 @ 24psi (350C) Flow rate: 200 uL/min Column: Pursuit XRS Diphenyl 100x 4.6mm 3umExample:Hydroxyalprazolam325>297 (Quant. Ion)325>216 (Qualifier)325>279 (Qualifier)
Extracted Spiked Plasma Benzo MRMChromatograms (10 ng/mL)Benzo results<strong>Opiates</strong> MethodExtracted Spiked Plasma Opiate MRMChromatograms (50ng/mL)Mobile Phase: 0.1% Formicaq/MeOHNebulizer Gas: N 2 @ 30psiDrying gas: N 2 @ 24psi (350C)Flow rate: 200 uL/minColumn: MetaChem Taxil 100 x2mm 3um
Opiate resultsCustom ReportsBenzodiazepine <strong>and</strong> <strong>Opiates</strong>SummaryExcellent sensitivityQuantitation limits will be below 10ng/mL (50ng for <strong>Opiates</strong>)Excellent quantitation can be achieved using a select fewinternal st<strong>and</strong>ardsBoth <strong>LC</strong> programs have a 15 minute run time.The additional sensitivity <strong>of</strong> 320ms allows for three ionmonitoring <strong>of</strong> each analyte.<strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> Amphetamines by<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>
Replicates 93 3 3 3 33002502001501005002 50 0 5 0 00 75 00Amount / Amt. Std.Rep lic ate s 24M15 012 510 07550250.999900 0.999925 0.999950 0.999975 1.000000 1.000025 1.000050 1.000075AmountAmphetamines Experimental ConditionsMethamphetamine: <strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong> BreakdownMethamphetamine Calibration CurveChromatographic data <strong>of</strong> AmphetaminesCalibration Curve ReportFile: e:\norchem\amps\amphetaminesdata multiplier2.mthDetector: 1200 Mass Spec, Address: 42Calibration Curve ReportFile: e:\norchem\amps\amphetaminesdata multiplier2.mthDetector: 1200 Mass Spec, Address: 42MethamphetamineC urve Fit: Linear, Origin: Ignore, Weight: None Resp. Fact. R SD : 5.318%y = +0.031914x +0.257271Coeff. Det.(r2): 0.997419Methamphetamine d5C urve Fit: Linear, Origin: Include (Ignore), W eight: N one Resp. Fact. R SD : 0.0000%y = +1.000000x +0.0C o eff. D et.( r2) : 1.00000 0Peak Size / PS Std.Peak SizeMethamphetamine 5-10,000 ng/mLMethamphetamine d5 ISSpiked: 50 ng/mL in urine
Amphetamine Summary Excellent sensitivity at the level <strong>of</strong> 5ng/mL Good separation from a column packed with afluorinated phenyl phase Detection limits will be at least the low ppb levels for allcompounds All 6 drugs can be run simultaneously in a 6 min. run Good linearity <strong>of</strong> calibration curves ranging from 5-10,000 ng/mL<strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> Carboxy-THCby<strong>LC</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>/<strong>MS</strong>Carboxy -THC Experimental ConditionsChromatograms – Carboxy - THC ESI Negative. <strong>LC</strong> Conditions: Column: Varian Pursuit Diphenyl50X2mm, 3μ Flow Rate: 0.2 mL/min A: Water B: Methanol Time %B 0:00 40 0:30 40 1:00 95 3:00 95 3:01 40 6:30 40 Injection Volume, 20 μL Mass Spec conditions: Argon pressure: 2.0 mtorr Q1/Q3 peak width: 1.0/1.0amu Transitions: 343.50 -> 299 CE 17.5 352.50 -> 308 CE 20.5 SamplesIn a complicated matrixsolutionSt<strong>and</strong>ard Solutions preparedby serial dilutions in DI water50 μL IS added to 1 mL <strong>of</strong>sampleCarboxy-THC – 10 ng/m<strong>LC</strong>arboxy-THC – 1 ng/mL
Carboxy -THC Calibration Curve ReportCarboxy -THC Sample Report ExampleCarboxy-THC 1-1000ng/m<strong>LC</strong>arboxy-THC d9 - ISCarboxy -THC Summary Excellent sensitivity at the 1 ng/mL Detection limits in the sub ppb levels Linear calibration curve from 1-1000 ng/mL R 2 value <strong>of</strong> 0.998 Run time <strong>of</strong> only 6.5 minutes