Space/time/frequency methods in adaptive radar - New Jersey ...
Space/time/frequency methods in adaptive radar - New Jersey ...
Space/time/frequency methods in adaptive radar - New Jersey ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
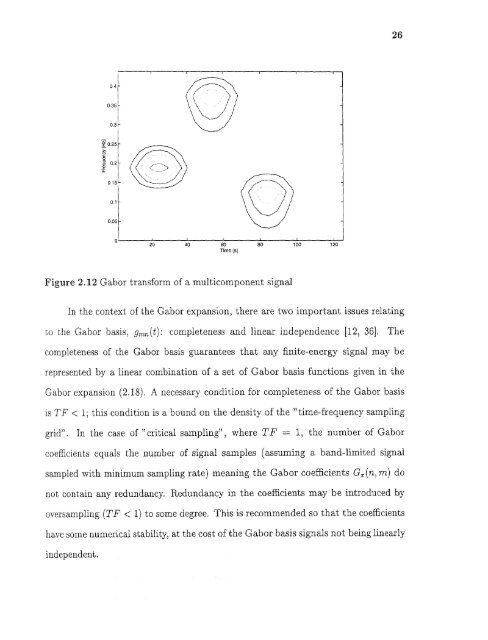
26Figure 2.12 Gabor transform of a multicomponent signalIn the context of the Gabor expansion, there are two important issues relat<strong>in</strong>gto the Gabor basis, gmn(t ): completeness and l<strong>in</strong>ear <strong>in</strong>dependence [12, 36]. Thecompleteness of the Gabor basis guarantees that any f<strong>in</strong>ite-energy signal may berepresented by a l<strong>in</strong>ear comb<strong>in</strong>ation of a set of Gabor basis functions given <strong>in</strong> theGabor expansion (2.18). A necessary condition for completeness of the Gabor basisis TF < 1; this condition is a bound on the density of the "<strong>time</strong>-<strong>frequency</strong> sampl<strong>in</strong>ggrid". In the case of "critical sampl<strong>in</strong>g" , where TF = 1, the number of Gaborcoefficients equals the number of signal samples (assum<strong>in</strong>g a band-limited signalsampled with m<strong>in</strong>imum sampl<strong>in</strong>g rate) mean<strong>in</strong>g the Gabor coefficients G x (n,m) donot conta<strong>in</strong> any redundancy. Redundancy <strong>in</strong> the coefficients may be <strong>in</strong>troduced byoversampl<strong>in</strong>g (TF < 1) to some degree. This is recommended so that the coefficientshave some numerical stability, at the cost of the Gabor basis signals not be<strong>in</strong>g l<strong>in</strong>early<strong>in</strong>dependent.