You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
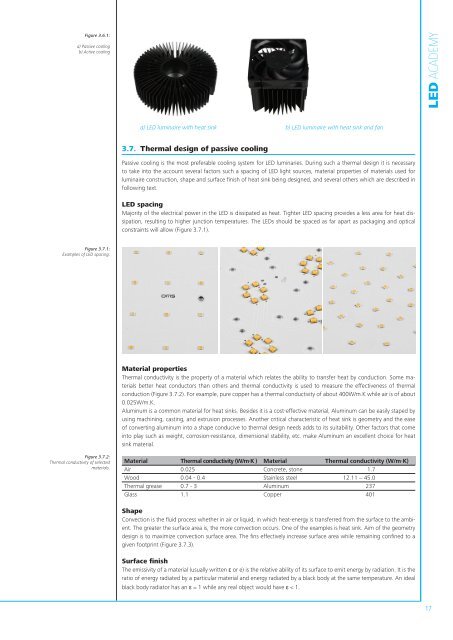
Figure 3.6.1:a) Passive coolingb) Active cooling<strong>LED</strong> <strong>ACADEMY</strong>a) <strong>LED</strong> luminaire with heat sink b) <strong>LED</strong> luminaire with heat sink and fan3.7. Thermal design of passive coolingPassive cooling is the most preferable cooling system for <strong>LED</strong> luminaries. During such a thermal design it is necessaryto take into the account several factors such a spacing of <strong>LED</strong> light sources, material properties of materials used forluminaire construction, shape and surface finish of heat sink being designed, and several others which are described infollowing text.<strong>LED</strong> spacingMajority of the electrical power in the <strong>LED</strong> is dissipated as heat. Tighter <strong>LED</strong> spacing provides a less area for heat dissipation,resulting to higher junction temperatures. The <strong>LED</strong>s should be spaced as far apart as packaging and opticalconstraints will allow (Figure 3.7.1).Figure 3.7.1:Examples of <strong>LED</strong> spacing.Material propertiesThermal conductivity is the property of a material which relates the ability to transfer heat <strong>by</strong> conduction. Some materialsbetter heat conductors than others and thermal conductivity is used to measure the effectiveness of thermalconduction (Figure 3.7.2). For example, pure copper has a thermal conductivity of about 400W/m.K while air is of about0.025W/m.K.Aluminum is a common material for heat sinks. Besides it is a cost-effective material, Aluminum can be easily staped <strong>by</strong>using machining, casting, and extrusion processes. Another critical characteristic of heat sink is geometry and the easeof converting aluminum into a shape conducive to thermal design needs adds to its suitability. Other factors that comeinto play such as weight, corrosion-resistance, dimensional stability, etc. make Aluminum an excellent choice for heatsink material.Figure 3.7.2:Thermal conductivity of selectedmaterials.Material Thermal conductivity (W/m·K ) Material Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)Air 0.025 Concrete, stone 1.7Wood 0.04 - 0.4 Stainless steel 12.11 ~ 45.0Thermal grease 0.7 - 3 Aluminum 237Glass 1.1 Copper 401ShapeConvection is the fluid process whether in air or liquid, in which heat-energy is transferred from the surface to the ambient.The greater the surface area is, the more convection occurs. One of the examples is heat sink. Aim of the geometrydesign is to maximize convection surface area. The fins effectively increase surface area while remaining confined to agiven footprint (Figure 3.7.3).Surface finishThe emissivity of a material (usually written ε or e) is the relative ability of its surface to emit energy <strong>by</strong> radiation. It is theratio of energy radiated <strong>by</strong> a particular material and energy radiated <strong>by</strong> a black body at the same temperature. An idealblack body radiator has an ε = 1 while any real object would have ε < 1.17