NEETS Module 8, Chapter 1
NEETS Module 8, Chapter 1
NEETS Module 8, Chapter 1
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
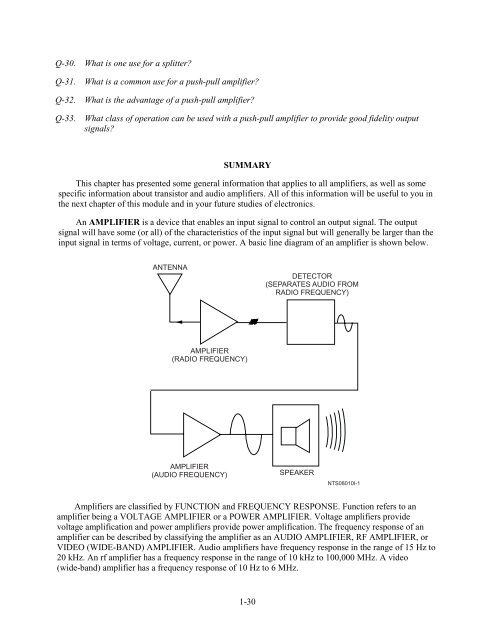
Q-30. What is one use for a splitter?Q-31. What is a common use for a push-pull amplifier?Q-32. What is the advantage of a push-pull amplifier?Q-33. What class of operation can be used with a push-pull amplifier to provide good fidelity outputsignals?SUMMARYThis chapter has presented some general information that applies to all amplifiers, as well as somespecific information about transistor and audio amplifiers. All of this information will be useful to you inthe next chapter of this module and in your future studies of electronics.An AMPLIFIER is a device that enables an input signal to control an output signal. The outputsignal will have some (or all) of the characteristics of the input signal but will generally be larger than theinput signal in terms of voltage, current, or power. A basic line diagram of an amplifier is shown below.ANTENNADETECTOR(SEPARATES AUDIO FROMRADIO FREQUENCY)AMPLIFIER(RADIO FREQUENCY)AMPLIFIER(AUDIO FREQUENCY)SPEAKERNTS08010I-1Amplifiers are classified by FUNCTION and FREQUENCY RESPONSE. Function refers to anamplifier being a VOLTAGE AMPLIFIER or a POWER AMPLIFIER. Voltage amplifiers providevoltage amplification and power amplifiers provide power amplification. The frequency response of anamplifier can be described by classifying the amplifier as an AUDIO AMPLIFIER, RF AMPLIFIER, orVIDEO (WIDE-BAND) AMPLIFIER. Audio amplifiers have frequency response in the range of 15 Hz to20 kHz. An rf amplifier has a frequency response in the range of 10 kHz to 100,000 MHz. A video(wide-band) amplifier has a frequency response of 10 Hz to 6 MHz.1-30