Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
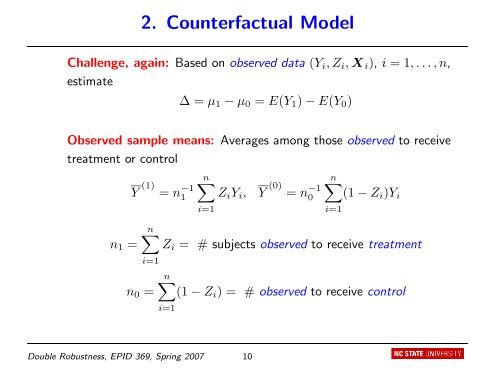
2. Counterfactual Model<br />
Challenge, aga<strong>in</strong>: Based on observed data (Yi, Zi, Xi), i = 1, . . . , n,<br />
estimate<br />
∆ = µ1 − µ0 = E(Y1) − E(Y0)<br />
Observed sample means: Averages among those observed to receive<br />
treatment or control<br />
n�<br />
n�<br />
(1 − Zi)Yi<br />
n1 =<br />
Y (1) = n −1<br />
1<br />
i=1<br />
ZiYi, Y (0) = n −1<br />
0<br />
i=1<br />
n�<br />
Zi = # subjects observed to receive treatment<br />
i=1<br />
n0 =<br />
n�<br />
(1 − Zi) = # observed to receive control<br />
i=1<br />
<strong>Double</strong> <strong>Robustness</strong>, EPID 369, Spr<strong>in</strong>g 2007 10