Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Double Robustness in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
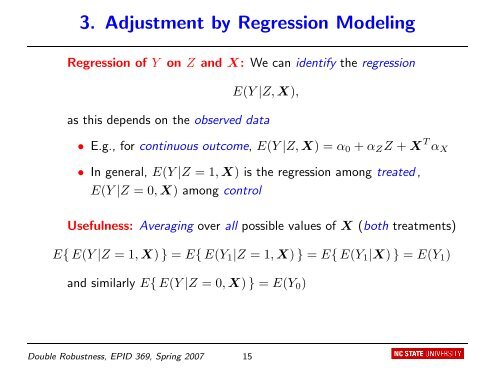
3. Adjustment by Regression Model<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Regression <strong>of</strong> Y on Z and X: We can identify the regression<br />
E(Y |Z, X),<br />
as this depends on the observed data<br />
• E.g., for cont<strong>in</strong>uous outcome, E(Y |Z, X) = α0 + αZZ + X T αX<br />
• In general, E(Y |Z = 1, X) is the regression among treated ,<br />
E(Y |Z = 0, X) among control<br />
Usefulness: Averag<strong>in</strong>g over all possible values <strong>of</strong> X (both treatments)<br />
E{ E(Y |Z = 1, X) } = E{ E(Y1|Z = 1, X) } = E{ E(Y1|X) } = E(Y1)<br />
and similarly E{ E(Y |Z = 0, X) } = E(Y0)<br />
<strong>Double</strong> <strong>Robustness</strong>, EPID 369, Spr<strong>in</strong>g 2007 15