Guidelines on surveillance among populations most at risk for HIV
Guidelines on surveillance among populations most at risk for HIV
Guidelines on surveillance among populations most at risk for HIV
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
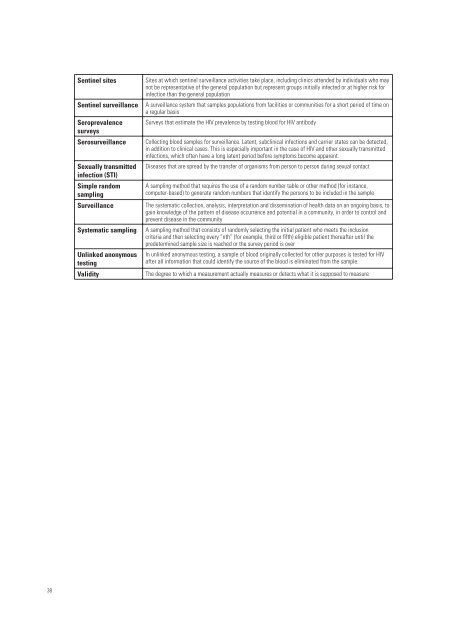
Sentinel sitesSentinel <strong>surveillance</strong>SeroprevalencesurveysSero<strong>surveillance</strong>Sexually transmittedinfecti<strong>on</strong> (STI)Simple randomsamplingSurveillanceSystem<strong>at</strong>ic samplingUnlinked an<strong>on</strong>ymoustestingValiditySites <strong>at</strong> which sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> activities take place, including clinics <strong>at</strong>tended by individuals who maynot be represent<strong>at</strong>ive of the general popul<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong> but represent groups initially infected or <strong>at</strong> higher <strong>risk</strong> <strong>for</strong>infecti<strong>on</strong> than the general popul<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong>A <strong>surveillance</strong> system th<strong>at</strong> samples popul<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong>s from facilities or communities <strong>for</strong> a short period of time <strong>on</strong>a regular basisSurveys th<strong>at</strong> estim<strong>at</strong>e the <strong>HIV</strong> prevalence by testing blood <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong> antibodyCollecting blood samples <strong>for</strong> <strong>surveillance</strong>. L<strong>at</strong>ent, subclinical infecti<strong>on</strong>s and carrier st<strong>at</strong>es can be detected,in additi<strong>on</strong> to clinical cases. This is especially important in the case of <strong>HIV</strong> and other sexually transmittedinfecti<strong>on</strong>s, which often have a l<strong>on</strong>g l<strong>at</strong>ent period be<strong>for</strong>e symptoms become apparent.Diseases th<strong>at</strong> are spread by the transfer of organisms from pers<strong>on</strong> to pers<strong>on</strong> during sexual c<strong>on</strong>tactA sampling method th<strong>at</strong> requires the use of a random number table or other method (<strong>for</strong> instance,computer-based) to gener<strong>at</strong>e random numbers th<strong>at</strong> identify the pers<strong>on</strong>s to be included in the sampleThe system<strong>at</strong>ic collecti<strong>on</strong>, analysis, interpret<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong> and dissemin<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong> of health d<strong>at</strong>a <strong>on</strong> an <strong>on</strong>going basis, togain knowledge of the p<strong>at</strong>tern of disease occurrence and potential in a community, in order to c<strong>on</strong>trol andprevent disease in the communityA sampling method th<strong>at</strong> c<strong>on</strong>sists of randomly selecting the initial p<strong>at</strong>ient who meets the inclusi<strong>on</strong>criteria and then selecting every “nth” (<strong>for</strong> example, third or fifth) eligible p<strong>at</strong>ient thereafter until thepredetermined sample size is reached or the survey period is overIn unlinked an<strong>on</strong>ymous testing, a sample of blood originally collected <strong>for</strong> other purposes is tested <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>after all in<strong>for</strong>m<strong>at</strong>i<strong>on</strong> th<strong>at</strong> could identify the source of the blood is elimin<strong>at</strong>ed from the sample.The degree to which a measurement actually measures or detects wh<strong>at</strong> it is supposed to measure38