3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
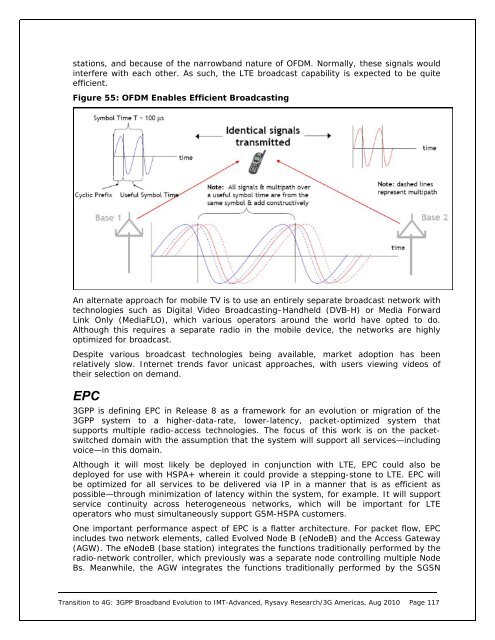
stations, and because of the narrowband nature of OFDM. Normally, these signals wouldinterfere with each other. As such, the LTE broadcast capability is expected <strong>to</strong> be quiteefficient.Figure 55: OFDM Enables Efficient BroadcastingAn alternate approach for mobile TV is <strong>to</strong> use an entirely separate broadcast network withtechnologies such as Digital Video Broadcasting–Handheld (DVB-H) or Media ForwardLink Only (MediaFLO), which various opera<strong>to</strong>rs around the world have opted <strong>to</strong> do.Although this requires a separate radio in the mobile device, the networks are highlyoptimized for broadcast.Despite various broadcast technologies being available, market adoption has beenrelatively slow. Internet trends favor unicast approaches, with users viewing videos oftheir selection on demand.EPC<strong>3GPP</strong> is defining EPC in Release 8 as a framework for an evolution or migration of the<strong>3GPP</strong> system <strong>to</strong> a higher-data-rate, lower-latency, packet-optimized system thatsupports multiple radio-access technologies. The focus of this work is on the packetswitcheddomain with the assumption that the system will support all services—includingvoice—in this domain.Although it will most likely be deployed in conjunction with LTE, EPC could also bedeployed for use with HSPA+ wherein it could provide a stepping-s<strong>to</strong>ne <strong>to</strong> LTE. EPC willbe optimized for all services <strong>to</strong> be delivered via IP in a manner that is as efficient aspossible—through minimization of latency within the system, for example. It will supportservice continuity across heterogeneous networks, which will be important for LTEopera<strong>to</strong>rs who must simultaneously support GSM-HSPA cus<strong>to</strong>mers.One important performance aspect of EPC is a flatter architecture. For packet flow, EPCincludes two network elements, called Evolved Node B (eNodeB) and the Access Gateway(AGW). The eNodeB (base station) integrates the functions traditionally performed by theradio-network controller, which previously was a separate node controlling multiple NodeBs. Meanwhile, the AGW integrates the functions traditionally performed by the SGSNTransition <strong>to</strong> <strong>4G</strong>: <strong>3GPP</strong> <strong>Broadband</strong> <strong>Evolution</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>IMT</strong>-<strong>Advanced</strong>, Rysavy Research/3G <strong>Americas</strong>, Aug 2010 Page 117