3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
3GPP Broadband Evolution to IMT-Advanced - 4G Americas
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
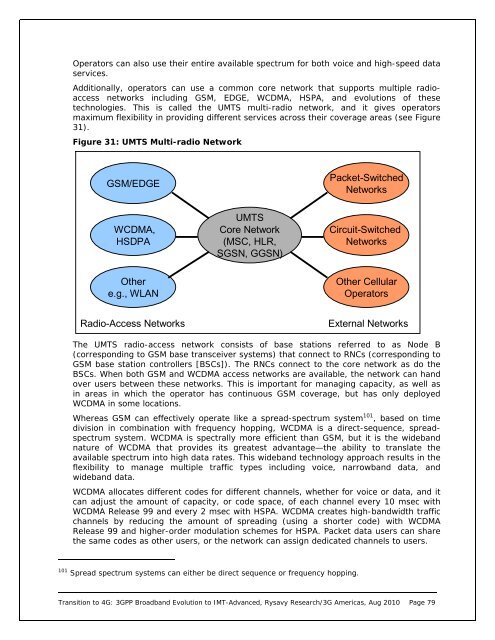
Opera<strong>to</strong>rs can also use their entire available spectrum for both voice and high-speed dataservices.Additionally, opera<strong>to</strong>rs can use a common core network that supports multiple radioaccessnetworks including GSM, EDGE, WCDMA, HSPA, and evolutions of thesetechnologies. This is called the UMTS multi-radio network, and it gives opera<strong>to</strong>rsmaximum flexibility in providing different services across their coverage areas (see Figure31).Figure 31: UMTS Multi-radio NetworkGSM/EDGEPacket-SwitchedNetworksWCDMA,HSDPAUMTSCore Network(MSC, HLR,SGSN, GGSN)Circuit-SwitchedNetworksOthere.g., WLANOther CellularOpera<strong>to</strong>rsRadio-Access NetworksExternal NetworksThe UMTS radio-access network consists of base stations referred <strong>to</strong> as Node B(corresponding <strong>to</strong> GSM base transceiver systems) that connect <strong>to</strong> RNCs (corresponding <strong>to</strong>GSM base station controllers [BSCs]). The RNCs connect <strong>to</strong> the core network as do theBSCs. When both GSM and WCDMA access networks are available, the network can handover users between these networks. This is important for managing capacity, as well asin areas in which the opera<strong>to</strong>r has continuous GSM coverage, but has only deployedWCDMA in some locations.Whereas GSM can effectively operate like a spread-spectrum system 101 , based on timedivision in combination with frequency hopping, WCDMA is a direct-sequence, spreadspectrumsystem. WCDMA is spectrally more efficient than GSM, but it is the widebandnature of WCDMA that provides its greatest advantage—the ability <strong>to</strong> translate theavailable spectrum in<strong>to</strong> high data rates. This wideband technology approach results in theflexibility <strong>to</strong> manage multiple traffic types including voice, narrowband data, andwideband data.WCDMA allocates different codes for different channels, whether for voice or data, and itcan adjust the amount of capacity, or code space, of each channel every 10 msec withWCDMA Release 99 and every 2 msec with HSPA. WCDMA creates high-bandwidth trafficchannels by reducing the amount of spreading (using a shorter code) with WCDMARelease 99 and higher-order modulation schemes for HSPA. Packet data users can sharethe same codes as other users, or the network can assign dedicated channels <strong>to</strong> users.101 Spread spectrum systems can either be direct sequence or frequency hopping.Transition <strong>to</strong> <strong>4G</strong>: <strong>3GPP</strong> <strong>Broadband</strong> <strong>Evolution</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>IMT</strong>-<strong>Advanced</strong>, Rysavy Research/3G <strong>Americas</strong>, Aug 2010 Page 79