2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
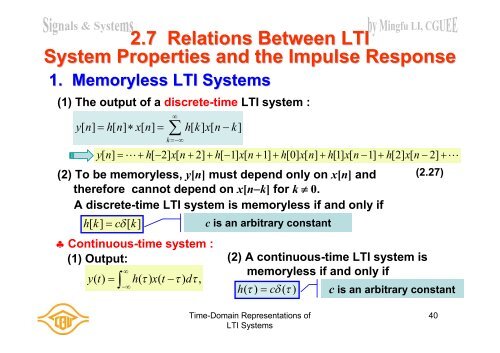
<strong>2.</strong>7 Relations Between <strong>LTI</strong>System Properties and the Impulse Response1. Memoryless <strong>LTI</strong> <strong>Systems</strong>(1) The output <strong>of</strong> a discrete-time <strong>LTI</strong> system :y[ n] h [ n] x [ n] h[ k] x[ n k]ky[n] h[ 2]x[n 2]h[ 1]x[n 1]h[0] x[n]h[1] x[n 1]h[2] x[n 2] (2) To be memoryless, y[n] must depend only on x[n] andtherefore cannot depend on x[nk] for k 0.A discrete-time <strong>LTI</strong> system is memoryless if and only ifh[ k] c [ k]Continuous-time system :(1) Output:y( t) h( ) x( t ) d,c is an arbitrary constant(2) A continuous-time <strong>LTI</strong> system ismemoryless if and only ifh( ) c ( )(<strong>2.</strong>27)c is an arbitrary constant<strong>Time</strong>-<strong>Domain</strong> <strong>Representations</strong> <strong>of</strong><strong>LTI</strong> <strong>Systems</strong>40