2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
2. Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
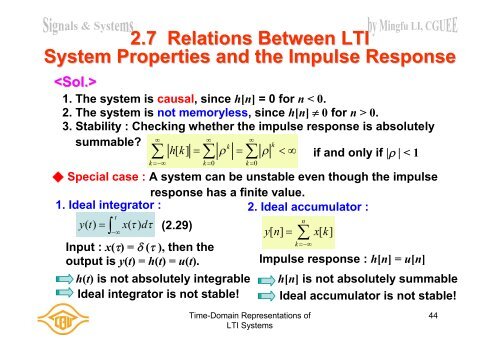
<strong>2.</strong>7 Relations Between <strong>LTI</strong>System Properties and the Impulse Response1. The system is causal, since h[n] = 0 for n < 0.<strong>2.</strong> The system is not memoryless, since h[n] 0 for n > 0.3. Stability : Checking whether the impulse response is absolutely summable?kkh[ k] if and only if < 1k k 0 k 0◆ Special case : A system can be unstable even though the impulseresponse has a finite value.1. Ideal integrator :<strong>2.</strong> Ideal accumulator : ty ( t)x()d(<strong>2.</strong>29)Input : x() = (), then theoutput is y(t) = h(t) = u(t).h(t) is not absolutely integrableIdeal integrator is not stable!nk y[ n] x[ k]Impulse response : h[n] = u[n]h[n] is not absolutely summableIdeal accumulator is not stable!<strong>Time</strong>-<strong>Domain</strong> <strong>Representations</strong> <strong>of</strong><strong>LTI</strong> <strong>Systems</strong>44