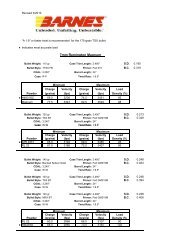
- Page 1 and 2: *FM 3-25.26 (FM 21-26)Field ManualN
- Page 3 and 4: Chapter7OVERLAYSPurposeMap OverlayA
- Page 5 and 6: AAppendixBMAP FOLDING TECHNIQUESApp
- Page 7 and 8: PART ONEMAP READINGCHAPTER 1TRAININ
- Page 9 and 10: CHAPTER 2MAPSCartography is the art
- Page 11 and 12: mission may depend on that map. All
- Page 13: Figure 2-2. Joint operations graphi
- Page 17 and 18: ectangle that represents the sheet
- Page 19 and 20: Figure 3-1. Topographical map.3-2.
- Page 21 and 22: shown in brown, rivers and lakes in
- Page 23 and 24: Figure 4-2. Reference lines.c. Geog
- Page 25 and 26: Figure 4-4. Determining latitude.(6
- Page 27 and 28: Figure 4-6. Determining geographic
- Page 29 and 30: • 5,125 x 300 = 1,537,500• 1,53
- Page 31 and 32: Figure 4-9. False eastings and nort
- Page 33 and 34: (1) Grid Lines. The regularly space
- Page 35 and 36: Figure 4-14. Coordinate scales.(a)
- Page 37 and 38: Figure 4-16. Placing a coordinate s
- Page 39 and 40: locations. With practice, this can
- Page 41 and 42: g. 10-Meter Identification. The gri
- Page 43 and 44: south to north. To designate any on
- Page 45 and 46: c. The situation may arise when a m
- Page 47 and 48: Figure 5-3. Transferring map distan
- Page 49 and 50: Figure 5-5. Measuring a curved line
- Page 51 and 52: Figure 5-7. Reading the extension s
- Page 53 and 54: about 30 inches long. To accurately
- Page 55 and 56: Factors AffectingRange EstimationTh
- Page 57 and 58: Figure 6-1. Three norths.b. Magneti
- Page 59 and 60: Figure 6-4. Measuring an azimuth.WA
- Page 61 and 62: . When using the protractor, the ba
- Page 63 and 64: azimuth to grid azimuth; the other,
- Page 65 and 66:
azimuth (Figure 6-12).Figure 6-12.
- Page 67 and 68:
Intersection is the location of an
- Page 69 and 70:
Figure 6-18. Resection with map and
- Page 71 and 72:
Figure 6-20. Modified resection.6-1
- Page 73 and 74:
(2) If you have observed any topogr
- Page 75 and 76:
(6) Map Reference. Reference is mad
- Page 77 and 78:
(3) The shape of the ground area co
- Page 79 and 80:
Figure 8-4. Low oblique photograph.
- Page 81 and 82:
Figure 8-7. Relationship of cameras
- Page 83 and 84:
8-5. SCALE DETERMINATIONBefore a ph
- Page 85 and 86:
square or rectangle. After the four
- Page 87 and 88:
. If no map is available, the shado
- Page 89 and 90:
Figure 8-17. Constructing a point d
- Page 91 and 92:
Figure 8-19. Locating the grid coor
- Page 93 and 94:
Figure 8-21. Side lap.b. The requir
- Page 95 and 96:
Figure 8-24. Placement of stereosco
- Page 97 and 98:
(2) Encasing the floating dial is a
- Page 99 and 100:
c. Presetting a Compass and Followi
- Page 101 and 102:
9-5. FIELD-EXPEDIENT METHODSFigure
- Page 103 and 104:
this, make a shadow clock and set y
- Page 105 and 106:
9-6. GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEMFigur
- Page 107 and 108:
CHAPTER 10ELEVATION AND RELIEFThe e
- Page 109 and 110:
contour line numbered 600. Locate p
- Page 111 and 112:
Figure 10-7. Uniform, steep slope.c
- Page 113 and 114:
Figure 10-11. Contour line around a
- Page 115 and 116:
Figure 10-15. Gradient.10-6. TERRAI
- Page 117 and 118:
Figure 10-19. Valley.(4) Ridge. A r
- Page 119 and 120:
Figure 10-24A. Cliff.Figure 10-24B.
- Page 121 and 122:
(3) To the south lies a valley; the
- Page 123 and 124:
Figure 10-28. Connecting points.(2)
- Page 125 and 126:
Figure 10-31. Drawing a hasty profi
- Page 127 and 128:
Figure 11-1. Map oriented with 11 d
- Page 129 and 130:
Figure 11-4. Map oriented with 10 d
- Page 131 and 132:
The key to success in land navigati
- Page 133 and 134:
(3) To The South. The terrain gentl
- Page 135 and 136:
concealment from enemy observation.
- Page 137 and 138:
compare the evidence you encounter
- Page 139 and 140:
(10) Because no one can move along
- Page 141 and 142:
ecommended. The point man is in fro
- Page 143 and 144:
Figure 12-1. Tracked vehicle capabi
- Page 145 and 146:
c. Use Terrain Features as Checkpoi
- Page 147 and 148:
(7) The distance factor in dead rec
- Page 149 and 150:
Table 13-1. Major desert regions.(1
- Page 151 and 152:
Mountains are generally understood
- Page 153 and 154:
Figure 13-3. Jungles and savannas.a
- Page 155 and 156:
trafficability, a deep accumulation
- Page 157 and 158:
CHAPTER 14UNIT SUSTAINMENTLand navi
- Page 159 and 160:
This sequence can be used to develo
- Page 161 and 162:
c. Area Sketches. These sketches in
- Page 163 and 164:
Figure B-2. How to slit and fold a
- Page 165 and 166:
1 degree = 1/360 circle = about 17.
- Page 167 and 168:
APPENDIX DJOINT OPERATIONS GRAPHICS
- Page 169 and 170:
APPENDIX FORIENTEERINGWhat is orien
- Page 171 and 172:
Figure F-2. A cross-country oriente
- Page 173 and 174:
(usually at one-minute intervals) t
- Page 175 and 176:
Figure F-5. Recorder's sheet.g. Eve
- Page 177 and 178:
F-8. CONTROL POINT GUIDELINESWhen t
- Page 179 and 180:
Figure F-9. Map symbols (continued)
- Page 181 and 182:
Figure F-9. Map symbols (continued)
- Page 183 and 184:
Figure F-9. Map symbols (continued)
- Page 185 and 186:
F-10. ORIENTEERING TECHNIQUESFigure
- Page 187 and 188:
APPENDIX GM2 COMPASSThe M2 compass
- Page 189 and 190:
APPENDIX HADDITIONAL AIDSThis appen
- Page 191 and 192:
H-6. GROUND-VEHICULAR LASER LOCATOR
- Page 193 and 194:
Step 3. Look at the composition. To
- Page 195 and 196:
J-5. COMPATABILITYAll GPS receivers
- Page 197 and 198:
• Signal intelligence.• Electro
- Page 199 and 200:
Figure K-4. Setup the units.d. The
- Page 201 and 202:
Figure K--10. Enter a way point.c.
- Page 203 and 204:
Figure K--14. Azimuth.d. The third
- Page 205 and 206:
GSRGTAG/VLLDground surveillance rad
- Page 207 and 208:
VNASvehicular navigation aids syste
- Page 209:
FM 3-25.26 (FM 21-26)20 JULY 2001By