Induction Motors
Induction Motors
Induction Motors
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
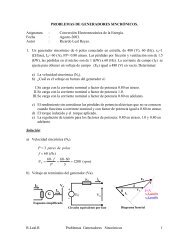
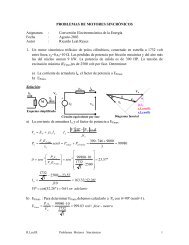
PART FOURINDUCTION MOTOR CONTROL . . .The Adjustable-Speed Magnetic DriveSquirrel-Cage Motor ControlsThe chart on page 21 illustrates the various methods of startingsquirrel-cage motors. The decision as to the type of startingdepends on the conditions of the installation from the standpointsof permissible current inrush from the power system,torque requirements of the load, and whether or not high torqueacceleration is objectionable to the driven machine.For large induction motors Magnetic Control has largely outmodedmanually-operated control. The remote control featurepermits mounting the starter near the motor, using shortmotor leads, with small control wires running to the pushbuttonstation or to pressure switch, float switch or other pilotdevice.Full Voltage (Across-the Line or “X”) Starters areuniversally used wherever the line capacity or generating capacitywill permit, and where full-voltage torque and acceleration isnot objectionable. Full-voltage starting equipment is easiest toinstall, operate and maintain, and has lowest first cost.For Low-Voltage <strong>Motors</strong>. Fig. 44 shows a typical acrossthe-linestarter. The starter is provided with under-voltage protectionand thermal overload relays. The combination starterprovides a disconnect switch, which is obtainable in the fusibleor non-fusible type, in combination with the starter.For Voltages above 600, control, such as shown in Fig.48, is commonly used.A control-circuit transformer supplies the low voltage for thepushbutton circuit and the closing circuit of the contactor. Inmany cases a time-delay undervoltage release type of pushbuttonstation is used to keep the control energized duringmomentary voltage dips.Short-Circuit Protection – In many locations the energyavailable from the power system in case of a ground orshort-circuit is more than can be interrupted by the motorstarter. Provision must then be made for interrupting the circuit,in case of a fault, without danger to personnel or excessivedamage to apparatus. This requirement is met for lowvoltagemotors with fused-type (Fig. 46) and circuit breakertype (Fig. 47) controls; and for high voltage motors, with the“Sa-Fuse” (high-interrupting-capacity, current-limiting fusecontrol), shown in Fig. 48, or high-interrupting-capacity oilor air circuit breaker control.In the “Sa-Fuse” Control, Fig. 48, current-limiting power fusesare used between the motor switch and the power circuit.These fuses limit short-circuit current to a value that can successfullybe interrupted by the fuses. The fault current is interruptedin 1/2 cycle or less, thus disconnecting the motor andcontrol so quickly as to minimize damage to the motor, andminimize the stresses on the control and the power system.Reversing, Across-the-Line Starting for squirrelcagemotors is accomplished by two magnetic contactors orswitches, one for forward rotation, the other for reverse rotation.A mechanical interlock is provided to prevent bothswitches from closing at the same time.Multispeed, Across-the-Line Starters consist of oneor more magnetic contactors or switches for each speed, whichrespond to pressing the pushbutton corresponding to the motorspeed desired. Overload protection is provided for each speedand the switches are mechanically interlocked to prevent theirclosing for one speed until they have opened for the other.Reduced Kva Starting – A popular, current-limitingstarting device for squirrel-cage motors up to approximately200 horsepower has been the well-known manually operatedCompensator, or the magnetic control shown in Fig. 45.The Compensator consists of an auto-transformer, providinga reduced voltage for starting, and a switching means bywhich the operator connects the motor first to the auto-transformerfor starting, and then to full line voltage for running.These operations are performed manually by throwing thelever to “start” and then to “run”. An interlock preventsthrowing the lever directly to “run” so the motor must bestarted on reduced voltage.On network systems, typically 120-208 volts, the starting currentis usually limited to increments of so many amperes persecond. Also, opening the circuit during starting is not permitted.In such cases the resistor type starter is commonly used.This starter uses a resistance in series with the motor windingswhich limits the current to an acceptable value. At suitabletime intervals successive amounts of series resistance are shortcircuiteduntil sufficient voltage is applied to permit the motorto start and accelerate. Compression type starters utilizinggraphite discs are also used for this purpose. Resistance typestarters may be either manually or magnetically operated.For high-voltage reduced kva starting, magnetically operatedcontrol is generally used. “Hi-Fuse” Control of the typeshown in Fig. 48 provides short-circuit protection.Wound-Rotor Motor ControlThe wound-rotor motor must have both primary and secondarycontrol.The primary control is an across-the-line starter of the type,and with protective features as discussed previously forsquirrel-cage motors.The secondary control usually have five to seven steps ofresistance. On the first step, with all the resistance in,approximately full-load starting torque is developed (see Fig.38) with slightly more than full-load current inrush.Additional steps of resistance are short circuited as the motorcomes up to speed. The normal operating condition is toshort circuit all external resistance.The secondary control may be either manual or magnetic inoperation. The manual controller is the familiar drum typecontrol with operating handle, shown in Fig. 52. Moving thehandle to the first starting position closes the line contactorthrough an interlock and places all the secondary resistanceacross the collector rings. Successive positions short-circuitout the resistor sections.Magnetic controls are pushbutton actuated where secondarycontrol is desired only to obtain low starting currentand to control acceleration. The contactors which 26