A Socially Assistive Robot Exercise Coach for the Elderly
A Socially Assistive Robot Exercise Coach for the Elderly
A Socially Assistive Robot Exercise Coach for the Elderly
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
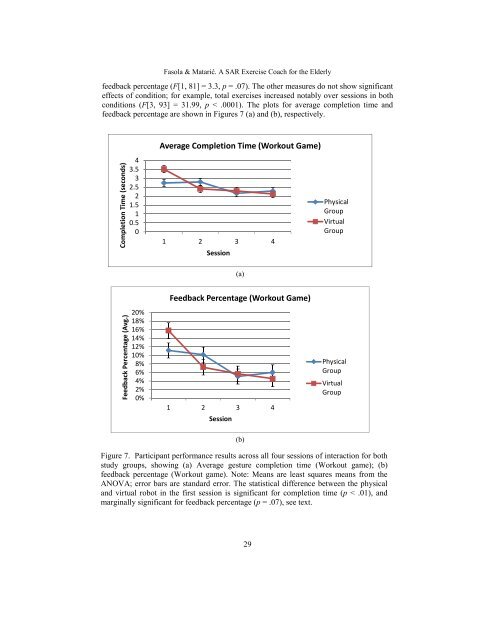
Fasola & Matarić. A SAR <strong>Exercise</strong> <strong>Coach</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Elderly</strong>feedback percentage (F[1, 81] = 3.3, p = .07). The o<strong>the</strong>r measures do not show significanteffects of condition; <strong>for</strong> example, total exercises increased notably over sessions in bothconditions (F[3, 93] = 31.99, p < .0001). The plots <strong>for</strong> average completion time andfeedback percentage are shown in Figures 7 (a) and (b), respectively.Average Completion Time (Workout Game)Completion Time (seconds)43.532.521.510.501 2 3 4SessionPhysicalGroupVirtualGroup(a)Feedback Percentage (Workout Game)Feedback Percentage (Avg.)20%18%16%14%12%10%8%6%4%2%0%1 2 3 4SessionPhysicalGroupVirtualGroup(b)Figure 7. Participant per<strong>for</strong>mance results across all four sessions of interaction <strong>for</strong> bothstudy groups, showing (a) Average gesture completion time (Workout game); (b)feedback percentage (Workout game). Note: Means are least squares means from <strong>the</strong>ANOVA; error bars are standard error. The statistical difference between <strong>the</strong> physicaland virtual robot in <strong>the</strong> first session is significant <strong>for</strong> completion time (p < .01), andmarginally significant <strong>for</strong> feedback percentage (p = .07), see text.29