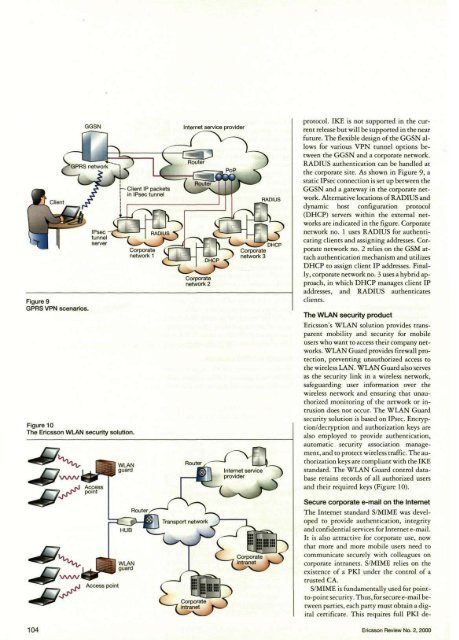
Figure 9GPRS VPN scenarios.Figure 10The Ericsson WLAN security solution.protocol. IKE is not supported in the currentrelease but will be supported in the nearfuture. The flexible design of the GGSN allowsfor various VPN tunnel options betweenthe GGSN and a corporate network.RADIUS authentication can be handled atthe corporate site. As shown in Figure 9, astatic IPsec connection is set up between theGGSN and a gateway in the corporate network.Alternative locations of RADIUS anddynamic host configuration protocol(DHCP) servers within the external networksare indicated in the figure. Corporatenetwork no. 1 uses RADIUS for authenticatingclients and assigning addresses. Corporatenetwork no. 2 relies on the GSM attachauthentication mechanism and utilizesDHCP to assign client IP addresses. Finally,corporate network no. 3 uses a hybrid approach,in which DHCP manages client IPaddresses, and RADIUS authenticatesclients.The WLAN security productEricsson's WLAN solution provides transparentmobility and security for mobileusers who want to access their <strong>com</strong>pany networks.WLAN Guard provides firewall protection,preventing unauthorized access tothe wireless LAN. WLAN Guard also servesas the security link in a wireless network,safeguarding user information over thewireless network and ensuring that unauthorizedmonitoring of the network or intrusiondoes not occur. The WLAN Guardsecurity solution is based on IPsec. Encryption/decryptionand authorization keys arealso employed to provide authentication,automatic security association management,and to protect wireless traffic. The authorizationkeys are <strong>com</strong>pliant with the IKEstandard. The WLAN Guard control databaseretains records of all authorized usersand their required keys (Figure 10).Secure corporate e-mail on the InternetThe Internet standard S/MIME was developedto provide authentication, integrityand confidential services for Internet e-mail.It is also attractive for corporate use, nowthat more and more mobile users need to<strong>com</strong>municate securely with colleagues oncorporate intranets. S/MIME relies on theexistence of a PKI under the control of atrusted CA.S/MIME is fundamentally used for pointto-pointsecurity. Thus, for secure e-mail betweenparties, each party must obtain a digitalcertificate. This requires full PKI de-104 Ericsson Review No. 2, 2000
ployment, which is a <strong>com</strong>plex task. Furthermore,for a mobile user on the Internetto use S/MIME to exchange e-mail withusers on the intranet, the corporate PKIneeds to be accessible from the Internet,which might conflict with corporate securitypolicies.Ericsson Research has designed a flexibleS/MIME-based architecture that employsdomain-to-point security. The solution allowsmobile users to manage corporate e-mail using an untrusted Internet e-mailserver; for example, at an ISP. The solutionrequires minimal PKI deployment, does notaffect the intranet infrastructure, and can beconstructed from standard <strong>com</strong>ponents(Figure 11).The CA issues digital certificates to mobileusers and to a secure mail gateway(SMG) that implements domain-to-pointsecurity for outgoing and in<strong>com</strong>ing e-mailbetween mobile and corporate users. E-mailfrom the intranet to the mobile user is automaticallysecured with S/MIME by theSMG, using the mobile user's certificate.Similarly, e-mail from the mobile user to auser on the intranet is automatically securedwith S/MIME on the mobile device (usingthe SMG's certificate) and forwarded to theSMG. Upon reception, the SMG restores thee-mail to its original form and forwards itto the intended recipient. An added benefitis that mobile users who do not know eachother's certificate can <strong>com</strong>municate securelyvia the SMG. This benefit can also be exploitedto distribute certificates.Future trendsThreats and opportunitiesIn the all-IP world, access will be separatedfrom services, and end-users will have a singlesubscription from which they can accessany service on the global Internet. Whilethis openness of access and services will increasethe value of the Internet, it will belike an open door to malicious users, fraudulentservice providers, and deceitful accessnetworks. Denial-of-service attacks mightdisturb IP traffic or destroy services. Threatsof this kind put strong security requirementson roaming, authentication, authorization,operation and management, andbilling. But the openness and service thatcan be furnished will also give operators andISPs new opportunities, such as the meansof providing security. For example, operatorsor ISPs might also function as CAs.Figure 11Secure corporate e-mail on the Internet.New solutionsThe mechanisms we have described will reducethe impact of new threats. In the future,firewalls and flexible trustmanagementengines will continue to beimportant security <strong>com</strong>ponents. These aregood tools in terms of protecting networksfrom denial-of-service attacks from the Internet.Attacks from terminals must bedealt with using encrypted radio links,ingress filtering firewalls, fraud detection,and auditing mechanisms. Cryptographicprotection of all control and managementtraffic in the network prevents unauthorizedusers from accessing core functionality inthe network. Protocols, such as IKE/IPsecand TLS, can be used as the basic protectionmechanism for several different applications.Likewise, necessary AAA mechanismsare required for reliable user authenticationand billing services. These mechanisms willprovide security for large-scale roaming,Ericsson Review No. 2, 2000 105