e-Waste Assessment Tanzania - e-Waste. This guide
e-Waste Assessment Tanzania - e-Waste. This guide
e-Waste Assessment Tanzania - e-Waste. This guide
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
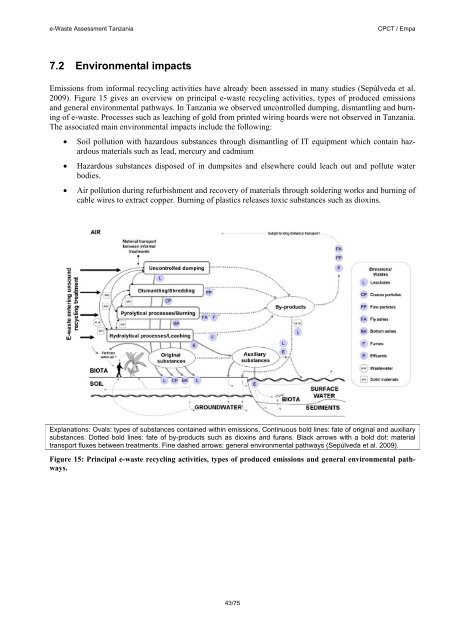
e-<strong>Waste</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>Tanzania</strong>CPCT / Empa7.2 Environmental impactsEmissions from informal recycling activities have already been assessed in many studies (Sepúlveda et al.2009). Figure 15 gives an overview on principal e-waste recycling activities, types of produced emissionsand general environmental pathways. In <strong>Tanzania</strong> we observed uncontrolled dumping, dismantling and burningof e-waste. Processes such as leaching of gold from printed wiring boards were not observed in <strong>Tanzania</strong>.The associated main environmental impacts include the following:Soil pollution with hazardous substances through dismantling of IT equipment which contain hazardousmaterials such as lead, mercury and cadmiumHazardous substances disposed of in dumpsites and elsewhere could leach out and pollute waterbodies.Air pollution during refurbishment and recovery of materials through soldering works and burning ofcable wires to extract copper. Burning of plastics releases toxic substances such as dioxins.Explanations: Ovals: types of substances contained within emissions. Continuous bold lines: fate of original and auxiliarysubstances. Dotted bold lines: fate of by-products such as dioxins and furans. Black arrows with a bold dot: materialtransport fluxes between treatments. Fine dashed arrows: general environmental pathways (Sepúlveda et al. 2009).Figure 15: Principal e-waste recycling activities, types of produced emissions and general environmental pathways.43/75