Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
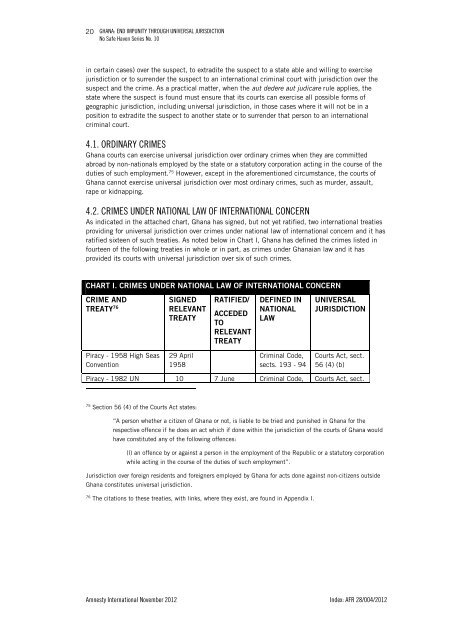
20GHANA: END IMPUNITY THROUGH UNIVERSAL JURISDICTIONNo Safe Haven Series No. 10in certain cases) over the suspect, to extradite the suspect to a state able and willing to exercisejurisdiction or to surrender the suspect to an international criminal court with jurisdiction over thesuspect and the crime. As a practical matter, when the aut dedere aut judicare rule applies, thestate where the suspect is found must ensure that its courts can exercise all possible forms ofgeographic jurisdiction, including universal jurisdiction, in those cases where it will not be in aposition to extradite the suspect to another state or to surrender that person to an internationalcriminal court.4.1. ORDINARY CRIMES<strong>Ghana</strong> courts can exercise universal jurisdiction over ordinary crimes when they are committedabroad by non-nationals employed by the state or a statutory corporation acting in the course of theduties of such employment. 75 However, except in the aforementioned circumstance, the courts of<strong>Ghana</strong> cannot exercise universal jurisdiction over most ordinary crimes, such as murder, assault,rape or kidnapping.4.2. CRIMES UNDER NATIONAL LAW OF INTERNATIONAL CONCERNAs indicated in the attached chart, <strong>Ghana</strong> has signed, but not yet ratified, two international treatiesproviding for universal jurisdiction over crimes under national law of international concern and it hasratified sixteen of such treaties. As noted below in Chart I, <strong>Ghana</strong> has defined the crimes listed infourteen of the following treaties in whole or in part, as crimes under <strong>Ghana</strong>ian law and it hasprovided its courts with universal jurisdiction over six of such crimes.CHART I. CRIMES UNDER NATIONAL LAW OF INTERNATIONAL CONCERNCRIME ANDTREATY 76SIGNEDRELEVANTTREATYRATIFIED/ACCEDEDTORELEVANTTREATYDEFINED INNATIONALLAWUNIVERSALJURISDICTIONPiracy - 1958 High SeasConvention29 April1958Criminal Code,sects. 193 - 94Courts Act, sect.56 (4) (b)Piracy - 1982 UN 10 7 June Criminal Code, Courts Act, sect.75Section 56 (4) of the Courts Act states:“A person whether a citizen of <strong>Ghana</strong> or not, is liable to be tried and punished in <strong>Ghana</strong> for therespective offence if he does an act which if done within the jurisdiction of the courts of <strong>Ghana</strong> wouldhave constituted any of the following offences:(l) an offence by or against a person in the employment of the Republic or a statutory corporationwhile acting in the course of the duties of such employment”.Jurisdiction over foreign residents and foreigners employed by <strong>Ghana</strong> for acts done against non-citizens outside<strong>Ghana</strong> constitutes universal jurisdiction.76The citations to these treaties, with links, where they exist, are found in Appendix I.<strong>Amnesty</strong> <strong>International</strong> November 2012 Index: AFR 28/004/2012