Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
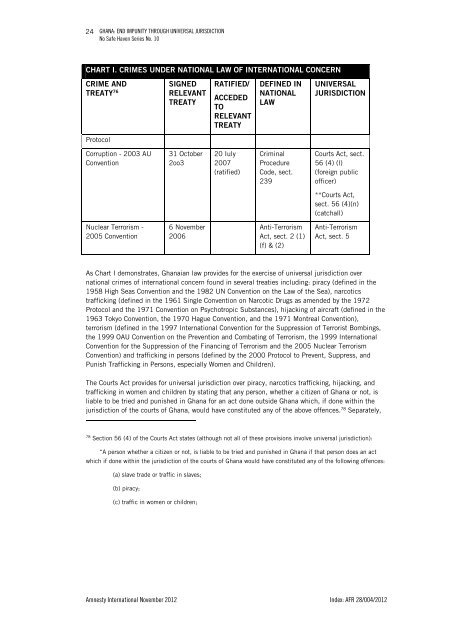
24GHANA: END IMPUNITY THROUGH UNIVERSAL JURISDICTIONNo Safe Haven Series No. 10CHART I. CRIMES UNDER NATIONAL LAW OF INTERNATIONAL CONCERNCRIME ANDTREATY 76SIGNEDRELEVANTTREATYRATIFIED/ACCEDEDTORELEVANTTREATYDEFINED INNATIONALLAWUNIVERSALJURISDICTIONProtocolCorruption - 2003 AUConvention31 October2oo320 Iuly2007(ratified)CriminalProcedureCode, sect.239Courts Act, sect.56 (4) (l)(foreign publicofficer)**Courts Act,sect. 56 (4)(n)(catchall)Nuclear Terrorism -2005 Convention6 November2006Anti-TerrorismAct, sect. 2 (1)(f) & (2)Anti-TerrorismAct, sect. 5As Chart I demonstrates, <strong>Ghana</strong>ian law provides for the exercise of universal jurisdiction overnational crimes of international concern found in several treaties including: piracy (defined in the1958 High Seas Convention and the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea), narcoticstrafficking (defined in the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs as amended by the 1972Protocol and the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances), hijacking of aircraft (defined in the1963 Tokyo Convention, the 1970 Hague Convention, and the 1971 Montreal Convention),terrorism (defined in the 1997 <strong>International</strong> Convention for the Suppression of Terrorist Bombings,the 1999 OAU Convention on the Prevention and Combating of Terrorism, the 1999 <strong>International</strong>Convention for the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism and the 2005 Nuclear TerrorismConvention) and trafficking in persons (defined by the 2000 Protocol to Prevent, Suppress, andPunish Trafficking in Persons, especially Women and Children).The Courts Act provides for universal jurisdiction over piracy, narcotics trafficking, hijacking, andtrafficking in women and children by stating that any person, whether a citizen of <strong>Ghana</strong> or not, isliable to be tried and punished in <strong>Ghana</strong> for an act done outside <strong>Ghana</strong> which, if done within thejurisdiction of the courts of <strong>Ghana</strong>, would have constituted any of the above offences. 78 Separately,78Section 56 (4) of the Courts Act states (although not all of these provisions involve universal jurisdiction):“A person whether a citizen or not, is liable to be tried and punished in <strong>Ghana</strong> if that person does an actwhich if done within the jurisdiction of the courts of <strong>Ghana</strong> would have constituted any of the following offences:(a) slave trade or traffic in slaves;(b) piracy;(c) traffic in women or children;<strong>Amnesty</strong> <strong>International</strong> November 2012 Index: AFR 28/004/2012