Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
Ghana - Amnesty International
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
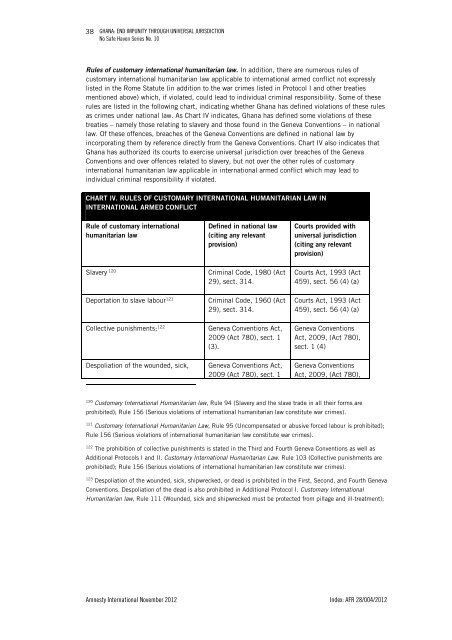
38GHANA: END IMPUNITY THROUGH UNIVERSAL JURISDICTIONNo Safe Haven Series No. 10Rules of customary international humanitarian law. In addition, there are numerous rules ofcustomary international humanitarian law applicable to international armed conflict not expresslylisted in the Rome Statute (in addition to the war crimes listed in Protocol I and other treatiesmentioned above) which, if violated, could lead to individual criminal responsibility. Some of theserules are listed in the following chart, indicating whether <strong>Ghana</strong> has defined violations of these rulesas crimes under national law. As Chart IV indicates, <strong>Ghana</strong> has defined some violations of thesetreaties – namely those relating to slavery and those found in the Geneva Conventions – in nationallaw. Of these offences, breaches of the Geneva Conventions are defined in national law byincorporating them by reference directly from the Geneva Conventions. Chart IV also indicates that<strong>Ghana</strong> has authorized its courts to exercise universal jurisdiction over breaches of the GenevaConventions and over offences related to slavery, but not over the other rules of customaryinternational humanitarian law applicable in international armed conflict which may lead toindividual criminal responsibility if violated.CHART IV. RULES OF CUSTOMARY INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW ININTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTRule of customary internationalhumanitarian lawDefined in national law(citing any relevantprovision)Courts provided withuniversal jurisdiction(citing any relevantprovision)Slavery 120Criminal Code, 1980 (Act29), sect. 314.Courts Act, 1993 (Act459), sect. 56 (4) (a)Deportation to slave labour 121Criminal Code, 1960 (Act29), sect. 314.Courts Act, 1993 (Act459), sect. 56 (4) (a)Collective punishments; 122Geneva Conventions Act,2009 (Act 780), sect. 1(3).Geneva ConventionsAct, 2009, (Act 780),sect. 1 (4)Despoliation of the wounded, sick,Geneva Conventions Act,2009 (Act 780), sect. 1Geneva ConventionsAct, 2009, (Act 780),120Customary <strong>International</strong> Humanitarian law, Rule 94 (Slavery and the slave trade in all their forms areprohibited); Rule 156 (Serious violations of international humanitarian law constitute war crimes).121Customary <strong>International</strong> Humanitarian Law, Rule 95 (Uncompensated or abusive forced labour is prohibited);Rule 156 (Serious violations of international humanitarian law constitute war crimes).122The prohibition of collective punishments is stated in the Third and Fourth Geneva Conventions as well asAdditional Protocols I and II. Customary <strong>International</strong> Humanitarian Law. Rule 103 (Collective punishments areprohibited); Rule 156 (Serious violations of international humanitarian law constitute war crimes).123Despoliation of the wounded, sick, shipwrecked, or dead is prohibited in the First, Second, and Fourth GenevaConventions. Despoliation of the dead is also prohibited in Additional Protocol I. Customary <strong>International</strong>Humanitarian law, Rule 111 (Wounded, sick and shipwrecked must be protected from pillage and ill-treatment);<strong>Amnesty</strong> <strong>International</strong> November 2012 Index: AFR 28/004/2012