Diesel distributor fuel-injection pumps VE - K-Jet.org
Diesel distributor fuel-injection pumps VE - K-Jet.org
Diesel distributor fuel-injection pumps VE - K-Jet.org
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
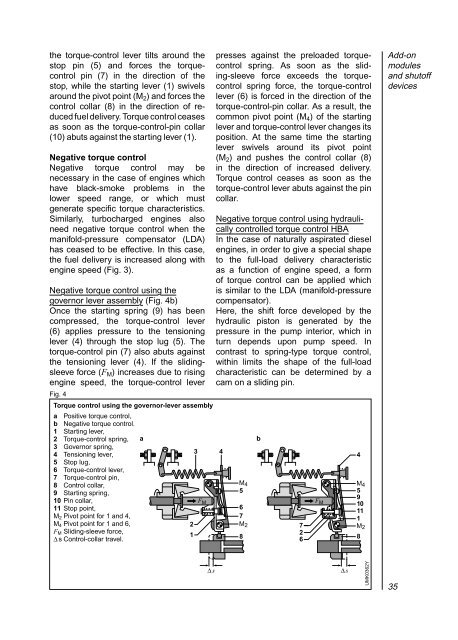
the torque-control lever tilts around thestop pin (5) and forces the torquecontrolpin (7) in the direction of thestop, while the starting lever (1) swivelsaround the pivot point (M 2 ) and forces thecontrol collar (8) in the direction of reduced<strong>fuel</strong> delivery. Torque control ceasesas soon as the torque-control-pin collar(10) abuts against the starting lever (1).Negative torque controlNegative torque control may benecessary in the case of engines whichhave black-smoke problems in thelower speed range, or which mustgenerate specific torque characteristics.Similarly, turbocharged engines alsoneed negative torque control when themanifold-pressure compensator (LDA)has ceased to be effective. In this case,the <strong>fuel</strong> delivery is increased along withengine speed (Fig. 3).Negative torque control using thegovernor lever assembly (Fig. 4b)Once the starting spring (9) has beencompressed, the torque-control lever(6) applies pressure to the tensioninglever (4) through the stop lug (5). Thetorque-control pin (7) also abuts againstthe tensioning lever (4). If the slidingsleeveforce (F M ) increases due to risingengine speed, the torque-control leverFig. 4Torque control using the governor-lever assemblya Positive torque control,b Negative torque control.1 Starting lever,2 Torque-control spring, a3 Governor spring,4 Tensioning lever,3 45 Stop lug,6 Torque-control lever,7 Torque-control pin,8 Control collar,9 Starting spring,10 Pin collar,11 Stop point,M 2 Pivot point for 1 and 4,M 4 Pivot point for 1 and 6,2F M Sliding-sleeve force,1∆ s Control-collar travel.presses against the preloaded torquecontrolspring. As soon as the sliding-sleeveforce exceeds the torquecontrolspring force, the torque-controllever (6) is forced in the direction of thetorque-control-pin collar. As a result, thecommon pivot point (M 4 ) of the startinglever and torque-control lever changes itsposition. At the same time the startinglever swivels around its pivot point(M 2 ) and pushes the control collar (8)in the direction of increased delivery.Torque control ceases as soon as thetorque-control lever abuts against the pincollar.Negative torque control using hydraulicallycontrolled torque control HBAIn the case of naturally aspirated dieselengines, in order to give a special shapeto the full-load delivery characteristicas a function of engine speed, a formof torque control can be applied whichis similar to the LDA (manifold-pressurecompensator).Here, the shift force developed by thehydraulic piston is generated by thepressure in the pump interior, which inturn depends upon pump speed. Incontrast to spring-type torque control,within limits the shape of the full-loadcharacteristic can be determined by acam on a sliding pin.M 4567M 28b726F M4M 45910111M 28Add-onmodulesand shutoffdevicesF M∆ s∆ sUMK0362Y35