Mission Operations Reference Model. Draft ... - CCSDS
Mission Operations Reference Model. Draft ... - CCSDS
Mission Operations Reference Model. Draft ... - CCSDS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
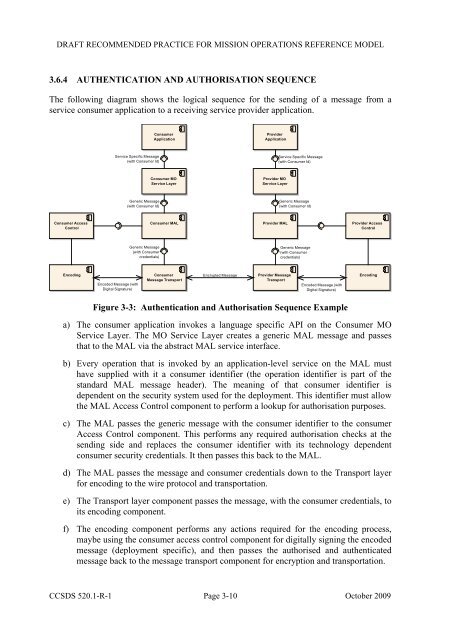
DRAFT RECOMMENDED PRACTICE FOR MISSION OPERATIONS REFERENCE MODEL3.6.4 AUTHENTICATION AND AUTHORISATION SEQUENCEThe following diagram shows the logical sequence for the sending of a message from aservice consumer application to a receiving service provider application.ConsumerApplicationProviderApplicationService Specific Message(with Consumer Id)Service Specific Message(with Consumer Id)Consumer MOService LayerProvider MOService LayerGeneric Message(with Consumer Id)Generic Message(with Consumer Id)Consumer AccessControlConsumer MALProvider MALProvider AccessControlGeneric Message(with Consumercredentials)Generic Message(with Consumercredentials)EncodingEncoded Message (withDigital Signature)ConsumerMessage TransportEncrypted MessageProvider MessageTransportEncoded Message (withDigital Signature)EncodingFigure 3-3: Authentication and Authorisation Sequence Examplea) The consumer application invokes a language specific API on the Consumer MOService Layer. The MO Service Layer creates a generic MAL message and passesthat to the MAL via the abstract MAL service interface.b) Every operation that is invoked by an application-level service on the MAL musthave supplied with it a consumer identifier (the operation identifier is part of thestandard MAL message header). The meaning of that consumer identifier isdependent on the security system used for the deployment. This identifier must allowthe MAL Access Control component to perform a lookup for authorisation purposes.c) The MAL passes the generic message with the consumer identifier to the consumerAccess Control component. This performs any required authorisation checks at thesending side and replaces the consumer identifier with its technology dependentconsumer security credentials. It then passes this back to the MAL.d) The MAL passes the message and consumer credentials down to the Transport layerfor encoding to the wire protocol and transportation.e) The Transport layer component passes the message, with the consumer credentials, toits encoding component.f) The encoding component performs any actions required for the encoding process,maybe using the consumer access control component for digitally signing the encodedmessage (deployment specific), and then passes the authorised and authenticatedmessage back to the message transport component for encryption and transportation.<strong>CCSDS</strong> 520.1-R-1 Page 3-10 October 2009