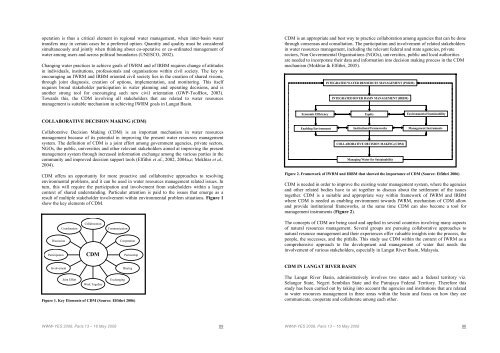
operation is thus a critical element in regional water management, when inter-basin watertransfers may in certain cases be a preferred option. Quantity and quality must be consideredsimultaneously and jointly when thinking about co-operative or co-ordinated management ofwater among users and across political boundaries (UNESCO, 2002).Changing water practices to achieve goals of IWRM and of IRBM requires change of attitudesin individuals, institutions, professionals and organisations within civil society. The key toencouraging an IWRM and IRBM oriented civil society lies in the creation of shared visions,through joint diagnosis, creation of options, implementation, and monitoring. This itselfrequires broad stakeholder participation in water planning and operating decisions, and isanother strong tool for encouraging such new civil orientation (GWP-ToolBox, 2003).Towards this, the CDM involving all stakeholders that are related to water resourcesmanagement is suitable mechanism in achieving IWRM goals in Langat Basin.COLLABORATIVE DECISION MAKING (CDM)Collaborative Decision Making (CDM) is an important mechanism in water resourcesmanagement because of its potential in improving the present water resources managementsystem. The definition of CDM is a joint effort among government agencies, private sectors,NGOs, the public, universities and other relevant stakeholders aimed at improving the presentmanagement system through increased information exchange among the various parties in thecommunity and improved decision support tools (Elfithri et al., 2002, 2004a,c; Mokhtar et al.,2004).CDM offers an opportunity for more proactive and collaborative approaches to resolvingenvironmental problems, and it can be used in water resources management related issues. Inturn, this will require the participation and involvement from stakeholders within a largercontext of shared understanding. Particular attention is paid to the issues that emerge as aresult of multiple stakeholder involvement within environmental problem situations. Figure 1show the key elements of CDM.CDM is an appropriate and best way to practice collaboration among agencies that can be donethrough consensus and consultation. The participation and involvement of related stakeholdersin water resources management, including the relevant federal and state agencies, privatesectors, Non Governmental Organisations (NGOs), universities, public and local authoritiesare needed to incorporate their data and information into decision making process in the CDMmechanism (Mokhtar & Elfithri, 2005).Economic Efficiency Equity Environmental SustainabilityEnabling EnvironmentINTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT (IWRM)INTEGRATED RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT (IRBM)Institutional FrameworksCOLLABORATIVE DECISION MAKING (CDM)Managing Water for SustainabilityManagement InstrumentsFigure 2. Framework of IWRM and IRBM that showed the importance of CDM (Source: Elfithri 2006)CDM is needed in order to improve the existing water management system, where the agenciesand other related bodies have to sit together to discuss about the settlement of the issuestogether. CDM is a suitable and appropriate way within framework of IWRM and IRBMwhere CDM is needed as enabling environment towards IWRM, mechanism of CDM allowand provide institutional frameworks, at the same time CDM can also become a tool formanagement instruments (Figure 2).DiscussionParticipationCoordinationCollaborationCDMCommunicationCooperationPartnershipThe concepts of CDM are being used and applied in several countries involving many aspectsof natural resources management. Several groups are pursuing collaborative approaches tonatural resource management and their experiences offer valuable insights into the process, thepeople, the successes, and the pitfalls. This study use CDM within the context of IWRM as acomprehensive approach to the development and management of water that needs theinvolvement of various stakeholders, especially in Langat River Basin, Malaysia.InvolvementSharingCDM IN LANGAT RIVER BASINJoint EffortExchangingWork TogetherFigure 1. Key Elements of CDM (Source: Elfithri 2006)The Langat River Basin, administratively involves two states and a federal territory viz.Selangor State, Negeri Sembilan State and the Putrajaya Federal Territory. Therefore thisstudy has been carried out by taking into account the agencies and institutions that are relatedto water resources management in three areas within the basin and focus on how they arecommunicate, cooperate and collaborate among each other.WWW-YES 2008, Paris 13 – 16 May 2008 89WWW-YES 2008, Paris 13 – 16 May 2008 90
This study uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods in assessing the CDM inLangat Basin, based on the concepts of structure and agency by Giddens (1984). A total of 40agencies that are related to water resources management in Langat Basin have beeninterviewed that include some of the federal and state government agencies, Local Authorities(LAs), private sector and Non Governmental Organisations (NGOs). Indepth-interviews havealso been carried out on five representatives of agencies in Langat Basin.Under the Malaysian Constitution, water is a state matter. Nevertheless when it comes to waterresources development, utilization and management, both the federal and state governmentsare involved. This is because the responsibility for water resource administration is fragmentedand is shared among a number of federal and state agencies, each of them have their ownspecific involvement in water related issues (Welch & Lim, 1987). Their interest in waterrelated matters could be viewed as from any one or more of the following three aspects:The planning, development and management of water resources aspect;The protection and conservation of water aspect;The land-use control and watershed management aspect.The Langat Basin is an area that drains by the Langat River in the state of Selangor, Malaysia.The Basin is currently the fastest developing area in the country. A number of large scalesocial-economic projects have either currently taking shape or are already completed in theBasin. This include the new township of Putrajaya (new Federal Government AdministrationCenter), Multi-Super Corridor (MSC) for the information technology industry, the BioValleyfor biotechnology research/industry, the Kuala Lumpur International airport and several otherinstitution of higher learning including universities. The rapid urbanisation in the Basin hasled to a large influx of people into the region. The sudden increase in population has exerted anumber of stresses on the Langat River. One of the main problems is river pollution fromsewage and suspended solids resulted from land clearing and discharge of untreated orincompletely treated sewage. The problem is a concern of many including government, nongovernmentalorganisations and the public as the Langat River is the main potable waterresource for the whole Langat Basin and the Klang Valley (Kuala Lumpur) nearby wherealmost a million people depend on the Langat for drinking water. Many solutions andactivities have been carried to arrest the deterioration of the Langat River water quality but fewhave achieved success. The root to the problem is the absent of a truly integrated managementsystem of water resources in the Basin (Elfithri, et al, 2004b). Figure 3 shows the map of theLangat River Basin.There are a number of government agencies, private sectors, local authorities, NGOs anduniversities that are involved in managing water resources in the Langat Basin and hadinitiated to a certain degree activities pertaining to realization of goals of an integrated waterresources management approach (Elfithri et al., 2004b). A study on CDM in Langat RiverBasin is carried out to analyse the current organizational structure in the basin and also to lookat several issues on CDM involving several agencies and institutions and the need of CDM tobe applied in this basin. The purpose of the research is also to seek common grounds fromwhich the diverse agencies can collaborate in managing the basin as well determining areas ofconflict.Figure 3. Map of the Langat River Basin, MalaysiaRESULTSThis study found that there is selective collaboration among agencies that are related to waterresources management in Langat Basin, in form of (i) meetings among agencies, (ii) process inmaking decision together, (iii) handling issues together, (iv) sharing the data and information,and (v) joint research projects among agencies.The level of application of CDM in Langat Basin have been assessed and found that most ofagencies had more involvement in term of management and administration (80%) and makingdecision together (80%), rather than handling issues together (67.5%), sharing the data andinformation (65%), and joint research projects among agencies (40%).The collaboration among agencies is influenced by the factors of structure and agency. It isfound that the factor of structure of administration and management is the main factor thatdrives and limits the collaboration process when compared to the factor of preparedness andcapacity of agency. Where it is found that the level of application of CDM in Langat Basin inall form of collaborations in Langat Basin are drives by the factor of structure ofadministration and management rather than the factor of preparedness and capacity of agency.The level of application of CDM in Langat Basin in form of management and administration,handling issues together and joint research projects among agencies are also limits by thefactor of structure of administration and management compared to the factor of preparednessand capacity of agency. But not in form of making decision together and sharing the data andinformation that limits by the factor of preparedness and capacity of agency itself.This study also found that there is no involvement from NGOs in water resources managementof Langat Basin (0%), lack of involvement from private sectors (40%), minimal involvementfrom government agencies in Federal Level (52%), and quiet enough involvement fromWWW-YES 2008, Paris 13 – 16 May 2008 91WWW-YES 2008, Paris 13 – 16 May 2008 92



![[pastel-00730831, v1] Incidence des pratiques d'entretien ... - LEESU](https://img.yumpu.com/50938896/1/184x260/pastel-00730831-v1-incidence-des-pratiques-dentretien-leesu.jpg?quality=85)











