Modelling Human Factors using the Systems Modelling Language
Modelling Human Factors using the Systems Modelling Language
Modelling Human Factors using the Systems Modelling Language
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
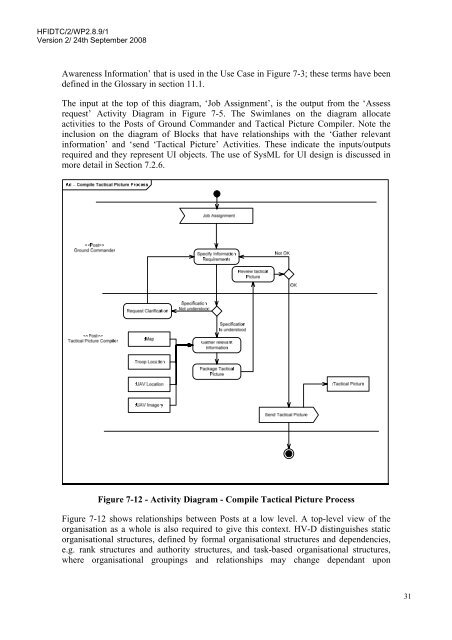
HFIDTC/2/WP2.8.9/1Version 2/ 24th September 2008Awareness Information’ that is used in <strong>the</strong> Use Case in Figure 7-3; <strong>the</strong>se terms have beendefined in <strong>the</strong> Glossary in section 11.1.The input at <strong>the</strong> top of this diagram, ‘Job Assignment’, is <strong>the</strong> output from <strong>the</strong> ‘Assessrequest’ Activity Diagram in Figure 7-5. The Swimlanes on <strong>the</strong> diagram allocateactivities to <strong>the</strong> Posts of Ground Commander and Tactical Picture Compiler. Note <strong>the</strong>inclusion on <strong>the</strong> diagram of Blocks that have relationships with <strong>the</strong> ‘Ga<strong>the</strong>r relevantinformation’ and ‘send ‘Tactical Picture’ Activities. These indicate <strong>the</strong> inputs/outputsrequired and <strong>the</strong>y represent UI objects. The use of SysML for UI design is discussed inmore detail in Section 7.2.6.Figure 7-12 - Activity Diagram - Compile Tactical Picture ProcessFigure 7-12 shows relationships between Posts at a low level. A top-level view of <strong>the</strong>organisation as a whole is also required to give this context. HV-D distinguishes staticorganisational structures, defined by formal organisational structures and dependencies,e.g. rank structures and authority structures, and task-based organisational structures,where organisational groupings and relationships may change dependant upon31