Peptidoglycan .Types of Bacterial Cell Walls and their Taxonomic ...
Peptidoglycan .Types of Bacterial Cell Walls and their Taxonomic ...
Peptidoglycan .Types of Bacterial Cell Walls and their Taxonomic ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Voi- 36, 1972 PEPTIDOGLYCAN TYPES OF BACTERIAL CELL WALLS<br />
439<br />
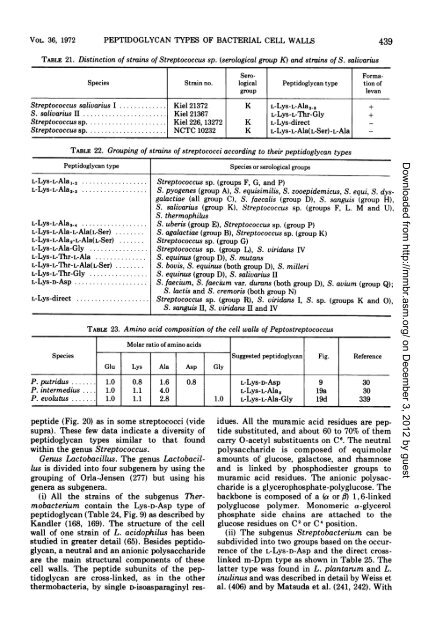
TABLE 21. Distinction <strong>of</strong> strains <strong>of</strong> Streptococcus sp. (serological group K) <strong>and</strong> strains <strong>of</strong> S. salivarius<br />
Sero- Forma-<br />
Species Strain no. logical <strong>Peptidoglycan</strong> type tion <strong>of</strong><br />
group levan<br />
Streptococcus salivarius I ............. Kiel 21372 K L-Lys-L-Ala2, +<br />
S. salivarius II ....................... Kiel 21367 L-Lys-L-Thr-Gly +<br />
Streptococcus sp...................... Kiel 226, 13272 K L-Lys-direct<br />
Streptococcus sp...................... NCTC 10232 K L-Lys-L-Ala(L-Ser)-L-Ala<br />
TABLE 22. Grouping <strong>of</strong> strains <strong>of</strong> streptococci according to <strong>their</strong> peptidoglycan types<br />
<strong>Peptidoglycan</strong> type Species or serological groups<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala,-2 ................... Streptococcus sp. (groups F, G, <strong>and</strong> P)<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala2,3 . .................. S. pyogenes (group A), S. equisimilis, S. zooepidemicus, S. equi, S. dysgalactiae<br />
(all group C), S. faecalis (group D), S. sanguis (group H),<br />
S. salivarius (group K), Streptococcus sp. (groups F, L. M <strong>and</strong> U),<br />
S. thermophilus<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala3 ..................... S. uberis (group E), Streptococcus sp. (group P)<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala-L-Ala(L-Ser) ........ S. agalactiae (group B), Streptococcus sp. (group K)<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala2-L-Ala(L-Ser) ....... Streptococcus sp. (group G)<br />
L-Lys-L-Ala-Gly ................ Streptococcus sp. (group L), S. viridans IV<br />
L-Lys-L-Thr-L-Ala .............. S. equinus (group D), S. mutans<br />
L-Lys-L-Thr-L-Ala(L-Ser) ........ S. bovis, S. equinus (both group D), S. milleri<br />
L-Lys-L-Thr-Gly ................ S. equinus (group D), S. salivarius II<br />
L-Lys-D-Asp .................... S. faecium, S. faecium var. durans (both group D), S. avium (group Q);<br />
S. lactis <strong>and</strong> S. cremoris (both group N)<br />
L-Lys-direct .. . ... Streptococcus sp. (group R), S. viridans I, S. sp. (groups K <strong>and</strong> 0),<br />
S. sanguis II, S. viridans II <strong>and</strong> IV<br />
TABLE 23. Amino acid composition <strong>of</strong> the cell walls <strong>of</strong> Peptostreptococcus<br />
Molar ratio <strong>of</strong> amino acids<br />
Species Suggested peptidoglycan Fig. Reference<br />
Glu Lys Ala Asp Gly<br />
P. putridus ....... 1.0 0.8 1.6 0.8 L-Lys-D-Asp 9 30<br />
P. intermedius .... 1.0 1.1 4.0 L-Lys-L-Ala2 19a 30<br />
P. evolutus ....... 1.0 1.1 2.8 1.0 L-Lys-L-Ala-Gly 19d 339<br />
peptide (Fig. 20) as in some streptococci (vide<br />
supra). These few data indicate a diversity <strong>of</strong><br />
peptidoglycan types similar to that found<br />
within the genus Streptococcus.<br />
Genus Lactobacillus. The genus Lactobacillus<br />
is divided into four subgenera by using the<br />
grouping <strong>of</strong> Orla-Jensen (277) but using his<br />
genera as subgenera.<br />
(i) All the strains <strong>of</strong> the subgenus Thermobacterium<br />
contain the Lys-D-Asp type <strong>of</strong><br />
peptidoglycan (Table 24, Fig. 9) as described by<br />
K<strong>and</strong>ler (168, 169). The structure <strong>of</strong> the cell<br />
wall <strong>of</strong> one strain <strong>of</strong> L. acidophilus has been<br />
studied in greater detail (65). Besides peptidoglycan,<br />
a neutral <strong>and</strong> an anionic polysaccharide<br />
are the main structural components <strong>of</strong> these<br />
cell walls. The peptide subunits <strong>of</strong> the peptidoglycan<br />
are cross-linked, as in the other<br />
thermobacteria, by single D-isoasparaginyl res-<br />
idues. All the muramic acid residues are peptide<br />
substituted, <strong>and</strong> about 60 to 70% <strong>of</strong> them<br />
carry 0-acetyl substituents on C6. The neutral<br />
polysaccharide is composed <strong>of</strong> equimolar<br />
amounts <strong>of</strong> glucose, galactose, <strong>and</strong> rhamnose<br />
<strong>and</strong> is linked by phosphodiester groups to<br />
muramic acid residues. The anionic polysaccharide<br />
is a glycerophosphate-polyglucose. The<br />
backbone is composed <strong>of</strong> a (a or f3) 1,6-linked<br />
polyglucose polymer. Monomeric a-glycerol<br />
phosphate side chains are attached to the<br />
glucose residues on C2 or C4 position.<br />
(ii) The subgenus Streptobacterium can be<br />
subdivided into two groups based on the occurrence<br />
<strong>of</strong> the L-Lys-D-Asp <strong>and</strong> the direct crosslinked<br />
m-Dpm type as shown in Table 25. The<br />
latter type was found in L. plantarum <strong>and</strong> L.<br />
inulinus <strong>and</strong> was described in detail by Weiss et<br />
al. (406) <strong>and</strong> by Matsuda et al. (241, 242). With<br />
Downloaded from<br />
http://mmbr.asm.org/<br />
on December 3, 2012 by guest