June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
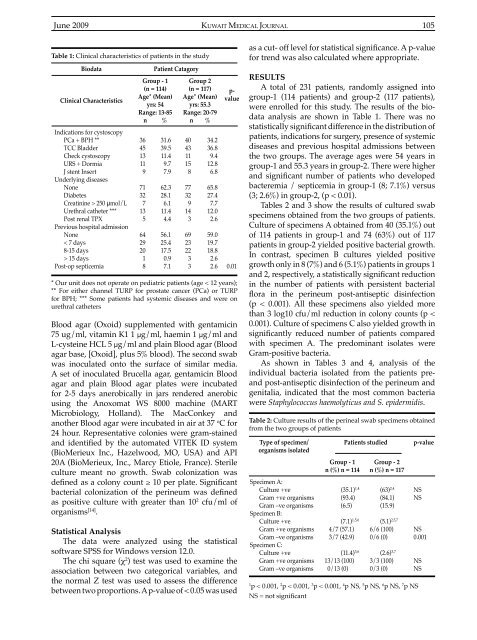
<strong>June</strong> 20<strong>09</strong>KUWAIT MEDICAL JOURNAL 105Table 1: Clinical characteristics of patients in the studyBiodataClinical CharacteristicsIndications for cystoscopyPCa + BPH **TCC BladderCheck cystoscopyURS + DormiaJ stent InsertUnderlying diseasesNoneDiabetesCreatinine > 250 µmol/LUrethral catheter ***Post renal TPXPrevious hospital admissionNone< 7 days8-15 days> 15 daysPost-op septicemiaPatient CatagoryGroup - 1(n = 114)Age* (Mean)yrs: 54Range: 13-85n %364513119713271356429201831.639.511.49.77.962.328.16.111.44.456.125.<strong>41</strong>7.50.97.1Group 2(n = 117)Age* (Mean)yrs: 55.3Range: 20-79n %p-valueBlood agar (Oxoid) supplemented with gentamicin75 ug/ml, vitamin K1 1 µg/ml, haemin 1 µg/ml andL-cysteine HCL 5 µg/ml and plain Blood agar (Bloodagar base, [Oxoid], plus 5% blood). The second swabwas inoculated onto the surface of similar media.A set of inoculated Brucella agar, gentamicin Bloodagar and plain Blood agar plates were incubatedfor 2-5 days anerobically in jars rendered anerobicusing the Anoxomat WS 8000 machine (MARTMicrobiology, Holland). The MacConkey andanother Blood agar were incubated in air at 37 o C for24 hour. Representative colonies were gram-stainedand identified by the automated VITEK ID system(BioMerieux Inc., Hazelwood, MO, USA) and API20A (BioMerieux, Inc., Marcy Etiole, France). Sterileculture meant no growth. Swab colonization wasdefined as a colony count ≥ 10 per plate. Significantbacterial colonization of the perineum was definedas positive culture with greater than 10 2 cfu/ml of<strong>org</strong>anisms [14] .Statistical AnalysisThe data were analyzed using the statisticalsoftware SPSS for Windows version 12.0.The chi square (χ 2 ) test was used to examine theassociation between two categorical variables, andthe normal Z test was used to assess the differencebetween two proportions. A p-value of < 0.05 was used404311158773291436923223334.236.89.<strong>41</strong>2.86.865.827.47.712.02.659.019.718.82.62.6 0.01* Our unit does not operate on pediatric patients (age < 12 years);** For either channel TURP for prostate cancer (PCa) or TURPfor BPH; *** Some patients had systemic diseases and were onurethral cathetersas a cut- off level for statistical significance. A p-valuefor trend was also calculated where appropriate.RESULTSA total of 231 patients, randomly assigned intogroup-1 (114 patients) and group-2 (117 patients),were enrolled for this study. The results of the biodataanalysis are shown in Table 1. There was nostatistically significant difference in the distribution ofpatients, indications for surgery, presence of systemicdiseases and previous hospital admissions betweenthe two groups. The average ages were 54 years ingroup-1 and 55.3 years in group-2. There were higherand significant number of patients who developedbacteremia / septicemia in group-1 (8; 7.1%) versus(3; 2.6%) in group-2, (p < 0.01).Tables 2 and 3 show the results of cultured swabspecimens obtained from the two groups of patients.Culture of specimens A obtained from 40 (35.1%) outof 114 patients in group-1 and 74 (63%) out of 117patients in group-2 yielded positive bacterial growth.In contrast, specimen B cultures yielded positivegrowth only in 8 (7%) and 6 (5.1%) patients in groups 1and 2, respectively, a statistically significant reductionin the number of patients with persistent bacterialflora in the perineum post-antiseptic disinfection(p < 0.001). All these specimens also yielded morethan 3 log10 cfu/ml reduction in colony counts (p