June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
June 09-41-2.indd - Kma.org.kw
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
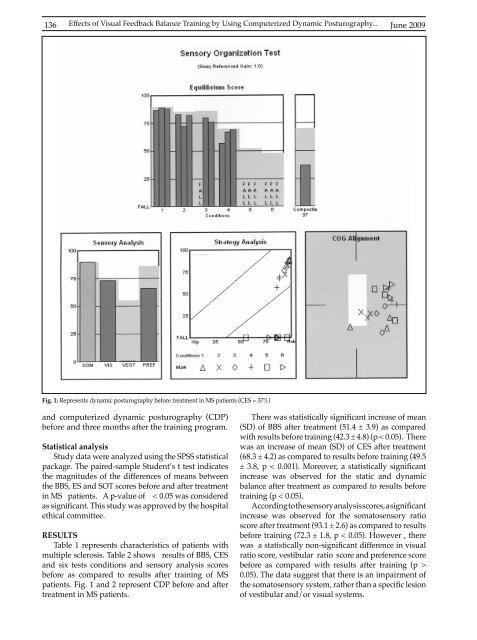
136Effects of Visual Feedback Balance Training by Using Computerized Dynamic Posturography...<strong>June</strong> 20<strong>09</strong>Fig. 1: Represents dynamic posturography before treatment in MS patients (CES = 37%)and computerized dynamic posturography (CDP)before and three months after the training program.Statistical analysisStudy data were analyzed using the SPSS statisticalpackage. The paired-sample Student’s t test indicatesthe magnitudes of the differences of means betweenthe BBS, ES and SOT scores before and after treatmentin MS patients. A p-value of < 0.05 was consideredas significant. This study was approved by the hospitalethical committee.RESULTSTable 1 represents characteristics of patients withmultiple sclerosis. Table 2 shows results of BBS, CESand six tests conditions and sensory analysis scoresbefore as compared to results after training of MSpatients. Fig. 1 and 2 represent CDP before and aftertreatment in MS patients.There was statistically significant increase of mean(SD) of BBS after treatment (51.4 ± 3.9) as comparedwith results before training (42.3 ± 4.8) (p < 0.05). Therewas an increase of mean (SD) of CES after treatment(68.3 ± 4.2) as compared to results before training (49.5± 3.8, p < 0.001). Moreover, a statistically significantincrease was observed for the static and dynamicbalance after treatment as compared to results beforetraining (p < 0.05).According to the sensory analysis scores, a significantincrease was observed for the somatosensory ratioscore after treatment (93.1 ± 2.6) as compared to resultsbefore training (72.3 ± 1.8, p < 0.05). However , therewas a statistically non-significant difference in visualratio score, vestibular ratio score and preference scorebefore as compared with results after training (p >0.05). The data suggest that there is an impairment ofthe somatosensory system, rather than a specific lesionof vestibular and/or visual systems.