Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
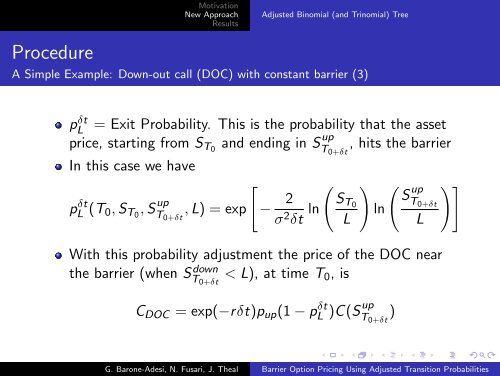
MotivationNew ApproachResults<strong>Adjusted</strong> Binomial (and Trinomial) TreeProcedureA Simple Example: Down-out call (DOC) with constant barrier (3)= Exit Probability. This is the probability that the assetprice, starting from S T0 and ending in S upT 0+δt, hits the barrierIn this case we have[ ( ) (pL δt (T 0, S T0 , S upT 0+δt, L) = exp − 2σ 2 δt ln S T0 Sup)]Tln0+δtL LpLδtWith this probability adjustment the price of the DOC nearthe barrier (when S downT 0+δt< L), at time T 0 , isC DOC = exp(−rδt)p up (1 − pL δt up)C(ST 0+δt)G. Barone-Adesi, N. Fusari, J. Theal <strong>Barrier</strong> <strong>Option</strong> <strong>Pricing</strong> <strong>Using</strong> <strong>Adjusted</strong> <strong>Transition</strong> <strong>Probabilities</strong>