Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
Barrier Option Pricing Using Adjusted Transition Probabilities
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
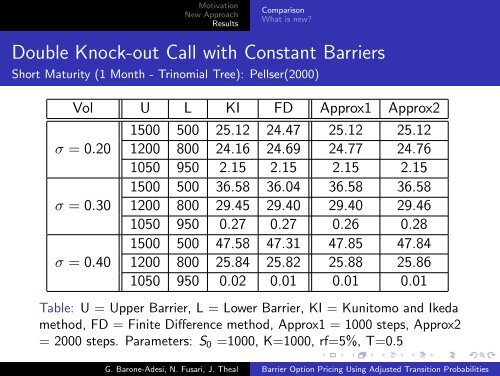
MotivationNew ApproachResultsComparisonWhat is new?Double Knock-out Call with Constant <strong>Barrier</strong>sShort Maturity (1 Month - Trinomial Tree): Pellser(2000)Vol U L KI FD Approx1 Approx21500 500 25.12 24.47 25.12 25.12σ = 0.20 1200 800 24.16 24.69 24.77 24.761050 950 2.15 2.15 2.15 2.151500 500 36.58 36.04 36.58 36.58σ = 0.30 1200 800 29.45 29.40 29.40 29.461050 950 0.27 0.27 0.26 0.281500 500 47.58 47.31 47.85 47.84σ = 0.40 1200 800 25.84 25.82 25.88 25.861050 950 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01Table: U = Upper <strong>Barrier</strong>, L = Lower <strong>Barrier</strong>, KI = Kunitomo and Ikedamethod, FD = Finite Difference method, Approx1 = 1000 steps, Approx2= 2000 steps. Parameters: S 0 =1000, K=1000, rf=5%, T=0.5G. Barone-Adesi, N. Fusari, J. Theal <strong>Barrier</strong> <strong>Option</strong> <strong>Pricing</strong> <strong>Using</strong> <strong>Adjusted</strong> <strong>Transition</strong> <strong>Probabilities</strong>