Post-transcriptional control of gene expression
Post-transcriptional control of gene expression
Post-transcriptional control of gene expression
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
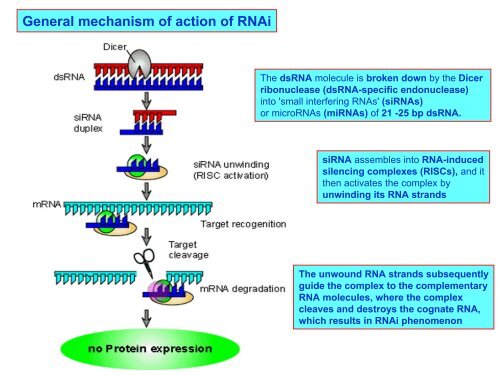
General mechanism <strong>of</strong> action <strong>of</strong> RNAiThe dsRNA molecule is broken down by the Dicerribonuclease (dsRNA-specific endonuclease)into 'small interfering RNAs' (siRNAs)or microRNAs (miRNAs) <strong>of</strong> 21 -25 bp dsRNA.siRNA assembles into RNA-inducedsilencing complexes (RISCs), and itthen activates the complex byunwinding its RNA strandsThe unwound RNA strands subsequentlyguide the complex to the complementaryRNA molecules, where the complexcleaves and destroys the cognate RNA,which results in RNAi phenomenon