D7 - Uro,Endocrine
D7 - Uro,Endocrine
D7 - Uro,Endocrine
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
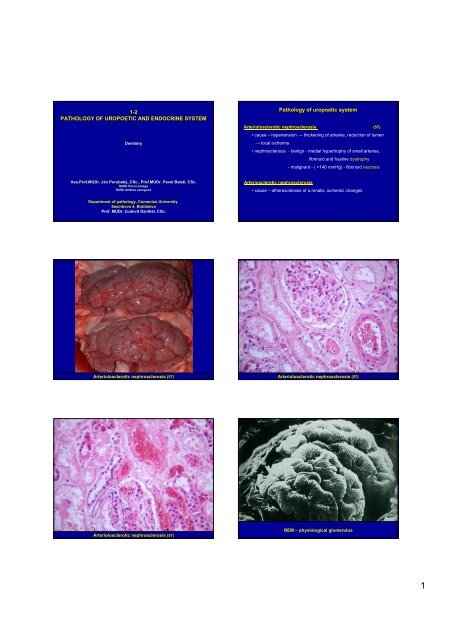
1-2PATHOLOGY OF UROPOETIC AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDentistryPathology of uropoetic systemArteriolosclerotic nephrosclerosis (57)• cause – hypertension → thickening of arteries, reduction of lumen→ local ischemia• nephrosclerosis - benign - medial hypertrophy of small arteries,fibrinoid and hyaline dystrophy- malignant - ( >140 mmHg) - fibrinoid necrosisAss.Prof.MUDr. . Ján J n Porubský, CSc., Prof.MUDr. Pavel Babál, , CSc.MUDr.Pavol JanegaMUDr.Andrea JanegováArteriosclerotic nephrosclerosis• cause – atherosclerosis of a.renalis, ischemic changesDepartment of pathology, Comenius UniversitySasinkova 4, BratislavaProf. MUDr. Ľudovít Danihel, CSc.Arteriolosclerotic nephrosclerosis (57) Arteriolosclerotic nephrosclerosis (57)Arteriolosclerotic nephrosclerosis (57)REM – physiological glomerulus1
EM – physiological glomerulus , REM – podocytes pediclesE – Endothelium, BM – Basal membrane, P- Podocyte, FP – Pedicles of the podocytesMesangial cellsPathology of uropoetic systemGlomerulonephritis (59,61)• renal disease characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli• cause – antibodies, IK (circulating, local formation)• acute / rapidly progressive / chronic• clinical presentation:- nephritic syndrome (hypertension, oedema, oliguria, hematuria)- nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, hypoalb., hyperlip., lipiduria,oedema)- combinationWhite arrow – subendothelial, Black arrow – subepithelial deposistsPathology of uropoetic systemGlomerulonephritis – morphological changesImmunofluoresence positivityMinimal change GN- no changes on light microscopy- on electron microscopy fusion of podocytes- nephrotic syndromeFocal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)- only some glomeruli within the kidney are affected and only aparts of a glomerulus- sclerosis of glomeruli and hyalinisation of arterioles- steroids are often not effective, often ending in renal failureMembranous glomerulonephritis- subepithel. "spike" deposits → thickening of BM- without cell proliferation2
thickening of glomerular capillaries /wire loops/Membranous glomerulonephritisMembranous glomerulonephritisthickening of glomerular capillaries /wire loops/Membranous glomerulonephritis (“spikes“)Pathology of uropoetic systemGlomerulonephritis – morphological changesProliferativeMesangial proliferative GN- IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease) – most common GN in adults- increased number of mesangial cells and matrix- IgA deposits in mesangium- macroscopic haematuriaEndocapillary GN- post-infectious (10-14d after streptococcal infection – group A β-hemolytic)- enlarged glomeruli, proliferating endothelial and mesangial cells +PMNL, Mo- nephritic syndromeMesangiocapillary (membranoproliferative) GN- proliferation of mesangial cells, matrix and thickening of capillariesglomerulus with prolifrating mesangila cellstubulsMesangial proliferative glomerulonephritisMembranoproliferative glomerulonephritis /IgG deposits/3
Pathology of uropoetic systemGlomerulonephritis – morphological changesExtracapillary (crescentic) GN- rapidly progressive GN- proliferation of epithelial cells of Bowman capsule → formation ofcrescents → compresion of capillaries- Goodpasture’s synd. - Ab against BM of glomeruli and alveoliDiffuse sclerosing GN and End stage kidney- advanced stage of all GN- glomerulosclerosis, sclerosis of small arteries, tubular atrophy,interstitial fibrosis…Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritisExtracapillary glomerulonephritisExtracapillary glomerulonephritissclerotic glomerulusEnd stage kidneyEnd stage kidney4
CASE REPORTCASE REPORT25-year-old woman• admitted to emergency room with feverand severe flank pain• history: 2 week lasting burning pain whileurinating, increased urinary frequencydiagnosis?diagnostic methods?• urinanalysis – increased leukocytes, slightly proteins• urine culture – E.coliPathology of uropoetic system?• acute pyelonephritisAcute tubointerstitial nephritis (acute pyelonephritis) (94)• E. coli, staphylococcuc aureus• ascending infection – reflux of the urine into the renal pelvis and calyces –bacteria entry into the renal parenchyma• abscess formation, purulent inflammatory exudate – in the collectingtubules and interstitial tissue• complications – urosepsis, pyonephros, peri- & pararenal abscess…abscessesabscessesAcute tubointerstitial nephritisAcute tubointerstitial nephritis5
enal pelvisinfiltrate of neutrophils in tubuli and renal interstitiumuretherAcute tubointerstitial nephritisAcute tubointerstitial nephritis (94)CASE REPORTabsces60-year-old manAcute tubointerstitial nephritis (94)CASE REPORT• presents to hospitel with dark-coloredurine and flank pain• history: low grade fever, lost 10kg in 3months, chronic smoker?diagnosis?diagnostic methods?• labs - polycythemia, urinanalysis - hematuria• USG, CT – 3x4cm mass on left kidney• biopsy• renal cell carcinoma6
Pathology of uropoetic systemTuRenal cell carcinoma (53)• Grawitz tumor, malignant, 80% renal tumors in adults• hematuria, flank and vague pain, palpable abdominal mass (in lessthan 10% of patients), paraneoplastic syndromes (EPO production)• multilobulated tumor, yellow-orange color, focal hemorrhage andnecrosis• clear cytoplasma cells – glycogen a lipidskidneyRenal cell carcinomaTu – neoplastic cells with abundant clear cytoplasmkidney tissueRenal cell carcinoma Renal cell carcinoma (53)Pathology of uropoetic systemundifferentiaited mesenchymal tissueNephroblastoma (Wilms’ tumor) (251)• most common solid tumor in young children (usually age before 4years)• chr 11 (WT1,2)• histologically 3 elements:- metanephric blastema- immature spindled cell stroma (muscle, cartilage, bone, fattissue, fibrous tissue)- immature epithelial elements (abortive tubules and glomeruli)undifferentiaited blastemaNephroblastoma (Wilms’ tumor) (251)7
Wilms Tu – immature tubules and glomeruliPathology of endocine systemDiabetes mellitus= metabolic disorder characterised by hyperglycemia due to substantiallyreduced or nonexists insulin secretion1.) Type I DM (total insuline deficiency)2.) Type II DM (relative insuline deficiency)3.) Other types of DM4.) Gestational DMNephroblastoma (Wilms’ tumor) (251)Complications:- acute: diabeticketoacidosis, nonketotichyperosmolar coma, hypoglycemia- chronic: macroangiopathy,microangiopathy (diabetic retinopathy,nefropathy), diabetic neuropathy, diabeticfootPathology of endocine systemDiabeticic nephropathy (159)- increase in mesangial matrix → glomerulosclerosis- diffuse- nodular (Kimmelstiel(Kimmelstiel-Wilsonsyndrome)- sclerosis of small arteries- Armani cells – prox. tubular cells filled glykogencalcificateGlomerulosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis (159)Glomerulosclerosis – hyalinisation (159) Glomerulosclerosis – Kimmelstiel Wilson disease (159)8
Pathology of endocrine systemThyroid gland goiterHashimoto’s disease (tyreoiditis) (240)- chronic lymphocytic tyreoiditis- lymphocytic infiltrate and follicles, oncocytes- autoimmune disease (TSH-R blocking Ab, other Ab, T-cells)- hypothyroidismHashimoto’s diseaselymphocytic infiltrate and lymphatic follicles with germinal centers replacing gland tissuelymphatic follicles with germinal centersHashimoto’s disease (240)Hashimoto’s disease (240)lymphatic follicle with germinal centerCASE REPORT35-year-old womanthyroid folliclesHashimoto’s disease (240)9
CASE REPORT• presents to hospital with palpitations,intolerance of heat, increased appetite• physical exam: exophthalmos, moistskin, pulse 110, diffusely enlargedthyroid glanddiagnosis?• labs – thyroid function testdiagnostic methods??• Graves disease• low TSH and high T3 and T4• scintigraphy – diffuse uptake of radioactive iodine• TSH-R antibodies presentPathology of endocrine systemThyroid gland goiterGraves - Basedow disease (70)- autoimmune disease (TSH-R stimulating Ab)- hyperthyroidism- hyperplasia of folicullar cells forming papillary projections into the lumen- depletion of colloid („moth-eaten“)1 cmGraves - Basedow diseaseprojections into the lumen of the thyroid folliclesprojections into the follicle lumen and scalloped colloid at the periphery adjacent to the follicular cellsGraves - Basedow disease (70)Graves - Basedow disease (70)10
Pathology of endocrine systemadrenal cortexPheochromocytoma(193)frequent in adults• neuroendocrine tumor of medulla of adrenal gland• secretes excessive amounts of catecholamines• hypertensive crisesPheochromocytoma (193)tumor cells with ample finely granular cytoplasm, nuclear atypiaPathology of endocrine systemCarcinoid (184)• neuroendocrine active tumor• colon, interstinum, bronchus, pancreas, other..• serotonin, calikrein... „carcinoid syndrome “Pheochromocytoma (193)• Skin flushing - The skin on face and upper chest changes colorfrom pink to red to purple with the feeling of „heat“. Flushing episodeslast from 30 to 60 seconds• Flushing can be provoked by eating or drinking alcohol• Facial skin lesions• Diarrhea. Frequent, watery stools accompanied by painfulabdominal cramps• Asthma-like signs and symptomssolid nests of uniform, small tumor cellsC A R C I N O I DmucosaCarcinoid in large intestineCarcinoid – colon (184)11
tumor cells with regular nuclei, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasmmucosal glandCARCINOIDCarcinoid – colon (184)12