priciples of insecticide use in rice ipm
priciples of insecticide use in rice ipm
priciples of insecticide use in rice ipm
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Insecticides <strong>in</strong> Rice IPM (DRR)<br />
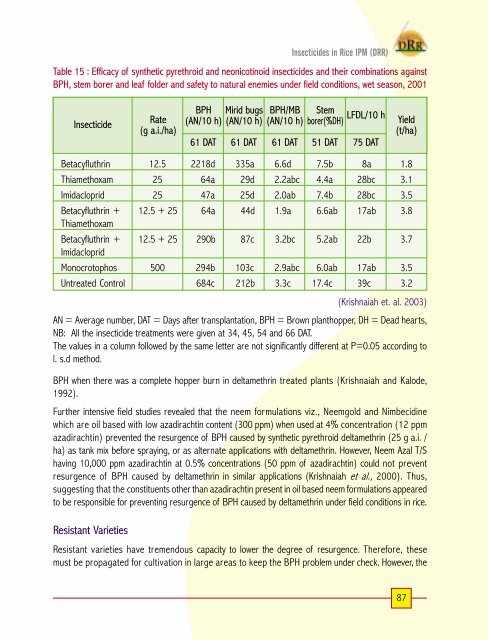
Table 15 : Efficacy <strong>of</strong> synthetic pyrethroid and neonicot<strong>in</strong>oid <strong><strong>in</strong>secticide</strong>s and their comb<strong>in</strong>ations aga<strong>in</strong>st<br />
BPH, stem borer and leaf folder and safety to natural enemies under field conditions, wet season, 2001<br />
Insecticide<br />
Rate<br />
(g a.i./ha)<br />
BPH Mirid bugs<br />
(AN/10 h) (AN/10 h)<br />
BPH/MB<br />
(AN/10 h)<br />
Stem<br />
LFDL/10 h<br />
borer(%DH)<br />
61 DAT 61 DAT 61 DAT 51 DAT 75 DAT<br />
Yield<br />
(t/ha)<br />
Betacyfluthr<strong>in</strong> 12.5 2218d 335a 6.6d 7.5b 8a 1.8<br />
Thiamethoxam 25 64a 29d 2.2abc 4.4a 28bc 3.1<br />
Imidacloprid 25 47a 25d 2.0ab 7.4b 28bc 3.5<br />
Betacyfluthr<strong>in</strong> +<br />
Thiamethoxam<br />
12.5 + 25 64a 44d 1.9a 6.6ab 17ab 3.8<br />
Betacyfluthr<strong>in</strong> +<br />
Imidacloprid<br />
12.5 + 25 290b 87c 3.2bc 5.2ab 22b 3.7<br />
Monocrotophos 500 294b 103c 2.9abc 6.0ab 17ab 3.5<br />
Untreated Control 684c 212b 3.3c 17.4c 39c 3.2<br />
(Krishnaiah et. al. 2003)<br />
AN = Average number, DAT = Days after transplantation, BPH = Brown planthopper, DH = Dead hearts,<br />
NB: All the <strong><strong>in</strong>secticide</strong> treatments were given at 34, 45, 54 and 66 DAT.<br />
The values <strong>in</strong> a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different at P=0.05 accord<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
l. s.d method.<br />
BPH when there was a complete hopper burn <strong>in</strong> deltamethr<strong>in</strong> treated plants (Krishnaiah and Kalode,<br />
1992).<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>tensive field studies revealed that the neem formulations viz., Neemgold and Nimbecid<strong>in</strong>e<br />
which are oil based with low azadiracht<strong>in</strong> content (300 ppm) when <strong>use</strong>d at 4% concentration (12 ppm<br />
azadiracht<strong>in</strong>) prevented the resurgence <strong>of</strong> BPH ca<strong>use</strong>d by synthetic pyrethroid deltamethr<strong>in</strong> (25 g a.i. /<br />
ha) as tank mix before spray<strong>in</strong>g, or as alternate applications with deltamethr<strong>in</strong>. However, Neem Azal T/S<br />
hav<strong>in</strong>g 10,000 ppm azadiracht<strong>in</strong> at 0.5% concentrations (50 ppm <strong>of</strong> azadiracht<strong>in</strong>) could not prevent<br />
resurgence <strong>of</strong> BPH ca<strong>use</strong>d by deltamethr<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> similar applications (Krishnaiah et al., 2000). Thus,<br />
suggest<strong>in</strong>g that the constituents other than azadiracht<strong>in</strong> present <strong>in</strong> oil based neem formulations appeared<br />
to be responsible for prevent<strong>in</strong>g resurgence <strong>of</strong> BPH ca<strong>use</strong>d by deltamethr<strong>in</strong> under field conditions <strong>in</strong> <strong>rice</strong>.<br />
Resistant Varieties<br />
Resistant varieties have tremendous capacity to lower the degree <strong>of</strong> resurgence. Therefore, these<br />
must be propagated for cultivation <strong>in</strong> large areas to keep the BPH problem under check. However, the<br />
87