Nigel Holt and Rob Lewis - Crown House Publishing.
Nigel Holt and Rob Lewis - Crown House Publishing.
Nigel Holt and Rob Lewis - Crown House Publishing.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
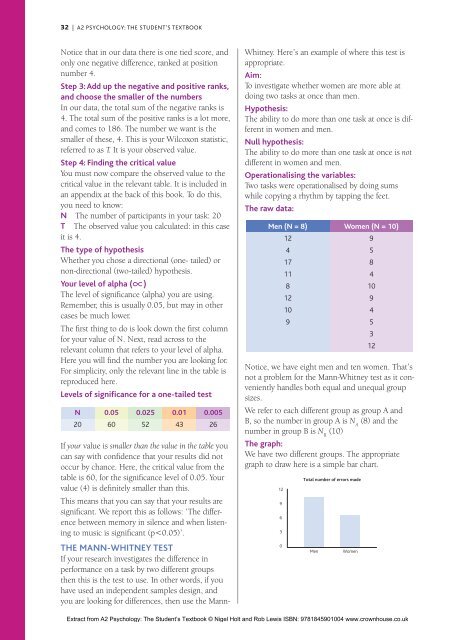
32 | A2 PSYCHOLOGY: THE STUDENT’S TEXTBOOKNotice that in our data there is one tied score, <strong>and</strong>only one negative difference, ranked at positionnumber 4.Step 3: Add up the negative <strong>and</strong> positive ranks,<strong>and</strong> choose the smaller of the numbersIn our data, the total sum of the negative ranks is4. The total sum of the positive ranks is a lot more,<strong>and</strong> comes to 186. The number we want is thesmaller of these, 4. This is your Wilcoxon statistic,referred to as T. It is your observed value.Step 4: Finding the critical valueYou must now compare the observed value to thecritical value in the relevant table. It is included inan appendix at the back of this book. To do this,you need to know:N The number of participants in your task: 20T The observed value you calculated: in this caseit is 4.The type of hypothesisWhether you chose a directional (one- tailed) ornon-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.Your level of alpha (∝)The level of significance (alpha) you are using.Remember, this is usually 0.05, but may in othercases be much lower.The first thing to do is look down the first columnfor your value of N. Next, read across to therelevant column that refers to your level of alpha.Here you will find the number you are looking for.For simplicity, only the relevant line in the table isreproduced here.Levels of significance for a one-tailed testN 0.05 0.025 0.01 0.00520 60 52 43 26If your value is smaller than the value in the table youcan say with confidence that your results did notoccur by chance. Here, the critical value from thetable is 60, for the significance level of 0.05. Yourvalue (4) is definitely smaller than this.This means that you can say that your results aresignificant. We report this as follows: ‘The differencebetween memory in silence <strong>and</strong> when listeningto music is significant (p