Chemistry_Today_April_2017_vk_com_stopthepress
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
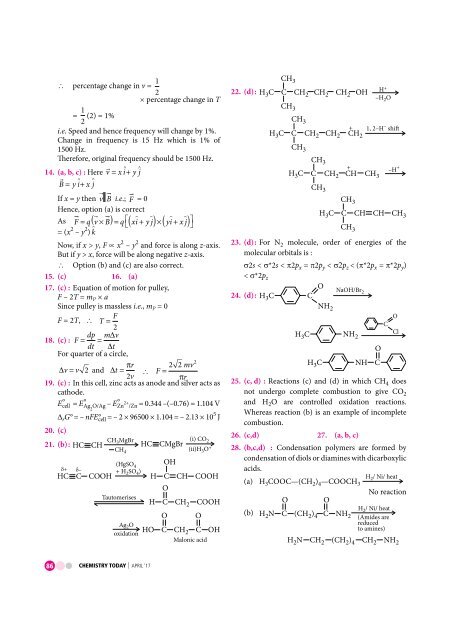
percentage change in v = 1 2<br />
<br />
percentage change in T<br />
= 1 (2) = 1%<br />
2<br />
i.e. Speed and hence frequency will change by 1%.<br />
Change in frequency is 15 Hz which is 1% of<br />
1500 Hz.<br />
Therefore, original frequency should be 1500 Hz.<br />
14. (a, b, c) : Here v = xi+<br />
y j<br />
<br />
B= yi ^<br />
+ x ^<br />
j<br />
<br />
If x = y then v B i.e.; F = 0<br />
Hence, option (a) is correct<br />
<br />
As F = q( v×<br />
B) = q⎡( xi ̂ + yj ̂)× ( yi ̂+<br />
xj ̂<br />
⎣<br />
) ⎤<br />
⎦<br />
= (x 2 – y 2 ) k̂<br />
^<br />
Now, if x > y, F ∝ x 2 – y 2 and force is along z-axis.<br />
But if y > x, force will be along negative z-axis.<br />
Option (b) and (c) are also correct.<br />
15. (c) 16. (a)<br />
17. (c) : Equation of motion for pulley,<br />
F – 2T = m P × a<br />
Since pulley is massless i.e., m P = 0<br />
F = 2T, T = F<br />
2<br />
dp m v<br />
18. (c) : F = = ∆<br />
dt ∆t<br />
For quarter of a circle,<br />
πr<br />
mv<br />
∆v= v 2 and ∆t<br />
= F = 2 2 2<br />
2v<br />
πr<br />
19. (c) : In this cell, zinc acts as anode and silver acts as<br />
cathode.<br />
E° cell = E° Ag2 O/Ag – E° 2+ Zn /Zn = 0.344 –(–0.76) = 1.104 V<br />
D r G° = – nFE° cell = – 2 × 96500 × 1.104 = – 2.13 × 10 5 J<br />
20. (c)<br />
CH3MgBr<br />
21. (b): HC CH HC CMgBr<br />
+ –<br />
HC C COOH<br />
CH 4<br />
^<br />
(HgSO 4<br />
+ H SO) 2 4<br />
Tautomerises<br />
Ag O 2<br />
oxidation<br />
OH<br />
(i) CO 2<br />
(ii)H 3 O+<br />
H C CH COOH<br />
O<br />
H C CH2<br />
COOH<br />
O O<br />
HO C CH C OH<br />
2<br />
Malonic acid<br />
CH 3<br />
22. (d):<br />
HC 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH H+<br />
2<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
–<br />
HC 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2<br />
–H O<br />
CH 3<br />
+ 1, 2–H shi<br />
CH 3<br />
HC 3 C CH 2 CH CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
+ –H +<br />
CH 3<br />
HC 3 C CH CH CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
23. (d): For N 2 molecule, order of energies of the<br />
molecular orbitals is :<br />
2s < *2s < 2p x = 2p y < p z < (*2p x = *2p y )<br />
< *2p z<br />
24. (d) : HC 3 C<br />
O<br />
NH 2<br />
NaOH/Br 2<br />
HC 3 NH 2<br />
C<br />
O<br />
HC 3 NH C<br />
25. (c, d) : Reactions (c) and (d) in which CH 4 does<br />
not undergo <strong>com</strong>plete <strong>com</strong>bustion to give CO 2<br />
and H 2 O are controlled oxidation reactions.<br />
Whereas reaction (b) is an example of in<strong>com</strong>plete<br />
<strong>com</strong>bustion.<br />
26. (c,d) 27. (a, b, c)<br />
28. (b,c,d) : Condensation polymers are formed by<br />
condensation of diols or diamines with dicarboxylic<br />
acids.<br />
(a) H 3 COOC—(CH 2 ) 4 —COOCH 3<br />
O<br />
(b) HN C (CH )<br />
O<br />
C NH<br />
2 2 4 2<br />
O<br />
Cl<br />
H/ Ni/ heat<br />
2<br />
No reaction<br />
H/ Ni/ heat<br />
2<br />
(Amides are<br />
reduced<br />
to amines)<br />
HN CH (CH ) CH NH<br />
2 2 24 2 2<br />
86 CHEMISTRY TODAY | APRIL ‘17