Chemistry_Today_April_2017_vk_com_stopthepress
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
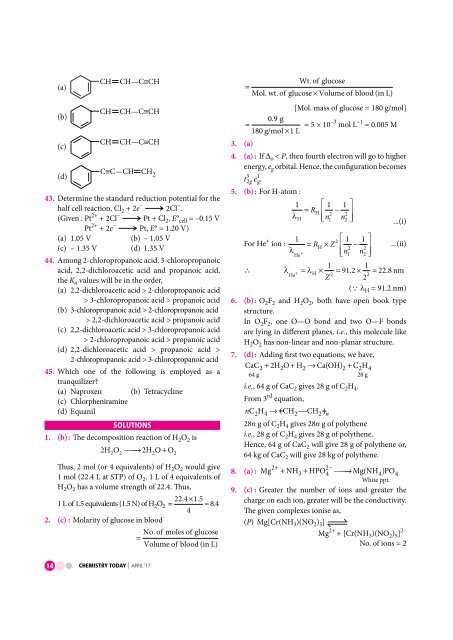
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
(c)<br />
(d)<br />
CH CH C CH<br />
CH CH C CH<br />
CH CH C CH<br />
C C—CH CH 2<br />
43. Determine the standard reduction potential for the<br />
half cell reaction, Cl 2 + 2e – 2Cl – .<br />
(Given : Pt 2+ + 2Cl – Pt + Cl 2 , E° cell = –0.15 V<br />
Pt 2+ + 2e – Pt, E° = 1.20 V)<br />
(a) 1.05 V<br />
(b) – 1.05 V<br />
(c) – 1.35 V (d) 1.35 V<br />
44. Among 2-chloropropanoic acid, 3-chloropropanoic<br />
acid, 2,2-dichloroacetic acid and propanoic acid,<br />
the K a values will be in the order,<br />
(a) 2,2-dichloroacetic acid > 2-chloropropanoic acid<br />
> 3-chloropropanoic acid > propanoic acid<br />
(b) 3-chloropropanoic acid > 2-chloropropanoic acid<br />
> 2,2-dichloroacetic acid > propanoic acid<br />
(c) 2,2-dichloroacetic acid > 3-chloropropanoic acid<br />
> 2-chloropropanoic acid > propanoic acid<br />
(d) 2,2-dichloroacetic acid > propanoic acid ><br />
2-chloropropanoic acid > 3-chloropropanoic acid<br />
45. Which one of the following is employed as a<br />
tranquilizer?<br />
(a) Naproxen (b) Tetracycline<br />
(c) Chlorpheniramine<br />
(d) Equanil<br />
SOLUTIONS<br />
1. (b): The de<strong>com</strong>position reaction of H 2 O 2 is<br />
2HO → 2HO+<br />
O<br />
2 2 2 2<br />
Thus, 2 mol (or 4 equivalents) of H 2 O 2 would give<br />
1 mol (22.4 L at STP) of O 2 . 1 L of 4 equivalents of<br />
H 2 O 2 has a volume strength of 22.4. Thus,<br />
22. 4×<br />
1.<br />
5<br />
1 L of 1.5 equivalents (1.5 N) of H 2 O 2 = = 8.4<br />
4<br />
2. (c) : Molarity of glucose in blood<br />
No.ofmoles of glucose<br />
=<br />
Volume of blood (inL)<br />
Wt.ofglucose<br />
=<br />
Mol. wt.ofglucose × Volume of blood (inL)<br />
[Mol. mass of glucose = 180 g/mol]<br />
09 . g<br />
=<br />
180 g/mol×<br />
1 L = 5 × 10–3 mol L –1 = 0.005 M<br />
3. (a)<br />
4. (a) : If ∆ o < P, then fourth electron will go to higher<br />
energy, e g orbital. Hence, the configuration be<strong>com</strong>es<br />
t 3 2g e 1 g.<br />
5. (b): For H-atom :<br />
1 1 1 <br />
= RH<br />
−<br />
2 2<br />
<br />
λ H <br />
n1<br />
n2<br />
<br />
...(i)<br />
For He + ion :<br />
1 <br />
2 1 1 <br />
= RH<br />
× Z −<br />
2 2<br />
...(ii)<br />
+ <br />
n<br />
1 n<br />
2 <br />
λ He<br />
1 1<br />
∴ λ + = λ<br />
He H<br />
× = 91. 2 × = 22.<br />
8 nm<br />
2 2<br />
Z 2<br />
( λ H = 91.2 nm)<br />
6. (b) : O 2 F 2 and H 2 O 2 , both have open book type<br />
structure.<br />
In O 2 F 2 , one O—O bond and two O—F bonds<br />
are lying in different planes, i.e., this molecule like<br />
H 2 O 2 has non-linear and non-planar structure.<br />
7. (d): Adding first two equations, we have,<br />
CaC2<br />
+ 2H2O+H2→ CaOH ( ) 2+<br />
C2H4<br />
64 g<br />
28 g<br />
i.e., 64 g of CaC 2 gives 28 g of C 2 H 4 .<br />
From 3 rd equation,<br />
nCH 2 4 → ( CH2CH2)<br />
n<br />
28n g of C 2 H 4 gives 28n g of polythene<br />
i.e., 28 g of C 2 H 4 gives 28 g of polythene.<br />
Hence, 64 g of CaC 2 will give 28 g of polythene or,<br />
64 kg of CaC 2 will give 28 kg of polythene.<br />
2+ 8. (a) : Mg NH3 HPO 2 −<br />
+ + 4 → MgNH ( 4)<br />
PO4<br />
White ppt.<br />
9. (c) : Greater the number of ions and greater the<br />
charge on each ion, greater will be the conductivity.<br />
The given <strong>com</strong>plexes ionise as,<br />
(P) Mg[Cr(NH 3 )(NO 2 ) 5 ]<br />
Mg 2+ + [Cr(NH 3 )(NO 2 ) 5 ] 2–<br />
No. of ions = 2<br />
14 CHEMISTRY TODAY | APRIL ‘17