- Page 2: FUNDAMENTALS OF ASTRODYNAMICS Roger
- Page 5 and 6: Copyright © 1971 by Dover Publicat
- Page 8 and 9: PREFACE The study of astrodynamics
- Page 10: acknowledgment is due Lieutenant Co
- Page 13 and 14: x 2.12 Improving a Preliminary Orbi
- Page 15 and 16: xii Appendix A Appendix B Appendix
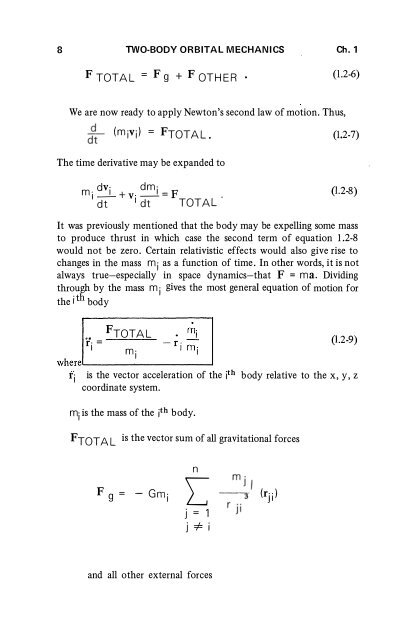
- Page 17 and 18: 2 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch.1 m
- Page 19 and 20: 4 LF=m r TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS
- Page 21: 6 lWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch . 1
- Page 25 and 26: 10 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS From
- Page 27 and 28: 12 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch. 1
- Page 29 and 30: 14 TWO·BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch.
- Page 31 and 32: 16 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch.1
- Page 33 and 34: 18 TWO·BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS, Ch.
- Page 35 and 36: 20 TWO·BODY ORBITAL MECHAN ICS Ch.
- Page 37 and 38: 22 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch .
- Page 39 and 40: 24 TWO -BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch_
- Page 41 and 42: 26 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS th. 1
- Page 43 and 44: 28 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHAN ICS and
- Page 45 and 46: 30 TWO·BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch .
- Page 47 and 48: 32 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch .
- Page 49 and 50: 34 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHAN ICS Ch.
- Page 51 and 52: 36 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS ell .
- Page 53 and 54: 38 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch .
- Page 55 and 56: 40 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch. 1
- Page 57 and 58: 42 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS I AU/
- Page 59 and 60: 44 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch .
- Page 61 and 62: 46 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHAN ICS Ch _
- Page 63 and 64: 48 TWO-BODY ORBITAL MECHANICS Ch. 1
- Page 66 and 67: CHAPTER 2 ORBIT DETERMINATION FROM
- Page 68 and 69: Sec. 2 .2 COORDINATE SYSTEMS 53 an
- Page 70 and 71: Sec. 2.2 vernal equinox direction C
- Page 72 and 73:
Sec. 2.2 COORDINATE SYSTEMS 57 star
- Page 74 and 75:
Sec. 2.3 CLASSICAL ORBITAL ELEMENTS
- Page 76 and 77:
Sec. 2.4 DETERMINING ORBITAL ElEMEN
- Page 78 and 79:
Sec. 2.4 DETERMINING ORBITAL ELEMEN
- Page 80 and 81:
Sec. VI DETERMINING ORBITAL ElEMENT
- Page 82 and 83:
Sec. 2.4 p:::: 1.5 DU e :::: O DETE
- Page 84 and 85:
Sec. 2.4 DETERMINING ORBITAL ELEMEN
- Page 86 and 87:
Sec. 2.5 DETERMINING r AND V Find t
- Page 88 and 89:
Sec. 2.5 DETERMINING r AND V 73 and
- Page 90 and 91:
Sec. 2.6 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS
- Page 92 and 93:
Sec. 2.6 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS
- Page 94 and 95:
Sec. 2.6 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS
- Page 96 and 97:
Sec. 2.6 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS
- Page 98 and 99:
Sec. 2.7 DETERMINATION FROM RADAR O
- Page 100 and 101:
Sec. 2.1 DETERMINATION FROM RADAR O
- Page 102 and 103:
Sec. 2.7 DETERMINATION FROM RADAR O
- Page 104 and 105:
Sec. 2.7 DETERMINATION FROM RADAR O
- Page 106 and 107:
Sec. 2.7 DETERMINATION FROM RADAR O
- Page 108 and 109:
Sec. 2.8 TRANSFORMATION USING AN EL
- Page 110 and 111:
Sec. 2.8 e quatorial buloe 21.4 km
- Page 112 and 113:
Sec:. 2.8 TRANSFOR MATION USING AN
- Page 114 and 115:
Sec. 2.8 TRANSFORMATION USING AN EL
- Page 116 and 117:
Sec. 2.9 THE MEASUREMENT OF TIME 10
- Page 118 and 119:
Sec. 2.9 THE MEASU REMENT OF TIME 1
- Page 120 and 121:
Sec. 2.9 THE MEASU REMENT OF TIME 1
- Page 122 and 123:
Sec. 2.9 THE MEASUREMENT OF TIME Fr
- Page 124 and 125:
Sec. 2.10 DETERMINATION FROM POSITI
- Page 126 and 127:
Sec. 2.10 DETERMINATION FROM POSITI
- Page 128 and 129:
Sec . 2.10 DETERMINATION FROM POSIT
- Page 130 and 131:
Sec. 2.10 DETERMINATION FROM POSITI
- Page 132 and 133:
Sec. 2.11 DETERMINATION FROM OPTICA
- Page 134 and 135:
Sec. 2.11 DETERMINATION FROM OPTICA
- Page 136 and 137:
Sec. 2.11 DETERMINATION FROM OPT IC
- Page 138 and 139:
Sec. 2.12 IMPROVING A PRELIMINARY O
- Page 140 and 141:
Sec. 2.12 IMPROV ING A PRELIMINARY
- Page 142 and 143:
Sec. 2. 12 IMPROVING A PRELIMINARY
- Page 144 and 145:
Sec. 2.12 IMPROV ING A PRELIMINARY
- Page 146 and 147:
Sec. 2.13 SPACE SU RVEILLANCE 131 R
- Page 148 and 149:
Sec. 2.14 TYPE AND LOCATION OF SENS
- Page 150 and 151:
Sec. 2.14 TYPE AND LO CATION OF SEN
- Page 152 and 153:
Sec. 2.14 TYPE AND LO CATION OF SEN
- Page 154 and 155:
Sec 2.14 TYPE AND LOCATION OF SENSO
- Page 156 and 157:
Sec. 20 15 GROUND TRACK OF A SATELL
- Page 158 and 159:
Sec. 2.15 GROUND TRACK OF A SATELLI
- Page 160 and 161:
Ch. 2 EXERC ISES 145 b. Object B de
- Page 162 and 163:
Ch.2 EX E RCISES 147 b. fl 0.707112
- Page 164 and 165:
Ch. 2 149 LIST OF REFERENCES 1. Gau
- Page 166 and 167:
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ORBITAL MANEUVERS B
- Page 168 and 169:
. Ul ILl ..J (I) i ;... , ..J
- Page 170 and 171:
Sec. 3.1 LOW ALTITUDE EARTH ORBITS
- Page 172 and 173:
Sec. 3.1 lOW ALTITUDE EARTH ORBITS
- Page 174 and 175:
Sec. 3.1 LOW ALTITUDE EARTH ORBITS
- Page 176 and 177:
Sec. 3.2 HIGH ALTITUDE EARTH ORBITS
- Page 178 and 179:
Sec. 3.3 IN-PLANE ORBIT CHANGES 163
- Page 180 and 181:
Sec. 3.3 IN-PLANE ORBIT CHANGES 165
- Page 182 and 183:
Sec. 3.3 I N-PLANE ORBIT CHANGES 16
- Page 184 and 185:
Sec. 3.4 OUT-O F-PLANE ORBIT CHANGE
- Page 186 and 187:
Sec. 3.4 OUT-OF-P lANE ORBIT CHANGE
- Page 188 and 189:
Sec. 3.4 OUT·O F·PLANE ORBIT CHAN
- Page 190 and 191:
Ch. 3 EXERCISES 175 8=0.56 c. & = -
- Page 192 and 193:
CHAPTER 4 POSITION AND VELOCITY AS
- Page 194 and 195:
Sec 4.1 HISTORICAL BACKGROUND 179 d
- Page 196 and 197:
Sec 4.2 TIME-OF-FLIGHT - ECCENTRIC
- Page 198 and 199:
Sec 4.2 TiME-OF-FLIGHT - ECCENTRIC
- Page 200 and 201:
Sec 4.2 TIME-OF-FLIGHT - ECCENTRIC
- Page 202 and 203:
Sec 4.2 TIME-O F-FLIGHT - ECCENTRIC
- Page 204 and 205:
Sec 4.2 TIME-OF-FLIGHT - ECCENTRIC
- Page 206 and 207:
Sec 4.3 UNIVERSAL FORMULATION - TIM
- Page 208 and 209:
Sec 4.4 THE PREDICTION PROBLEM But
- Page 210 and 211:
4.4 SUbsti: u: n : : q a[: ' : # 19
- Page 212 and 213:
Sec 4.4 THE PREDICTION PROBLEM 197
- Page 214 and 215:
Sec 4 .4 THE PREDICTiON PROBLEM 199
- Page 216 and 217:
Sec 4.4 we obtain THE PREDICTION PR
- Page 218 and 219:
Sec 4.5 UNIVERSAL VARIABLE FORMU LA
- Page 220 and 221:
Sec 4.5 UNIVERSAL VARIABLE FORMU LA
- Page 222 and 223:
Sec 4 .5 UNIVERSAL VAR IABLE FORMUL
- Page 224 and 225:
Sec 4.5 UNIVERSAL VARIABLE FORMULAT
- Page 226 and 227:
Sec 4.5 UNIVERSAL VARIABLE FORMULAT
- Page 228 and 229:
Sec 4.6 THE KEPLER PROBLEM 213 Figu
- Page 230 and 231:
Sec 4.6 THE KEPLER PROBLEM 2 1 5 Fr
- Page 232 and 233:
Sec 4.6 THE KEPLER PROBLEM 217 rang
- Page 234 and 235:
Sec 4.6 THE KEPLER PROBLEM 219 4;6.
- Page 236 and 237:
Sec 4.6 THE KEPLER PROBLEM 221 atte
- Page 238 and 239:
Ch. 4 EXERCISES 223 Calculate the t
- Page 240 and 241:
Ch. 4 EXERCISES 225 (t - to) 0 (t -
- Page 242 and 243:
,CHAPTER S ORBIT DETERMINATION FROM
- Page 244 and 245:
Sec. 5.2 THE GAUSS PROBLEM - SO LUT
- Page 246 and 247:
Sec. 5.3 SO LUTION VIA UNIVERSAL VA
- Page 248 and 249:
Sec. 5.3 SO LUTION VIA UNIVERSAL VA
- Page 250 and 251:
Sec. 5.3 SO LUTiON VIA UNIVERSAL VA
- Page 252 and 253:
Sec. 5.3 SOLUTION VIA UNIVERSALVAR
- Page 254 and 255:
Sec. 5.3 SO LUTION VIA UNIVERSAL VA
- Page 256 and 257:
Sec. 5.4 THE p-ITERATION METHOD 241
- Page 258 and 259:
Sec. 5.4 THE p-ITERATION METHOD 243
- Page 260 and 261:
Sec. 5.4 THE p-ITERATION METHOD 245
- Page 262 and 263:
Sec. 5.4 THE p-ITERATION METHOD 247
- Page 264 and 265:
Sec. 5.4 THE p-ITERATION M ETHOD 24
- Page 266 and 267:
Sec. 5.5 GAUSS PROBLEM USING f AND
- Page 268 and 269:
1 and G o = O. 5.5.1 Development of
- Page 270 and 271:
Sec. 5.5 GAUSS PROBLEM _ USINGf AND
- Page 272 and 273:
Sec. 5.5 GAUSS PROBLEM USING f ANDg
- Page 274 and 275:
Sec. 5.6 TH E ORIGINAL GAUSS METHOD
- Page 276 and 277:
Sec. 5.6 THE ORIGINAL GAUSS METHOD
- Page 278 and 279:
Sec. 5.6 THE ORIGINAL GAUSS METHOD
- Page 280 and 281:
Sec. 5.7 INTERCEPT AND RENDEZVOUS 5
- Page 282 and 283:
Sec. 5.7 INTERCEPT AND RENDEZVOUS 2
- Page 284 and 285:
Sec. 5.7 INTERCEPT AND RENDEZVOUS 2
- Page 286 and 287:
Sec. 5.8 DETERMINATION OF ORBIT 271
- Page 288 and 289:
Ch. 5 EXERCISES 273 Z, x, Y, Z, whi
- Page 290:
Ch. 5 EXERCISES Compare the accurac
- Page 293 and 294:
278 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 295 and 296:
280 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 297 and 298:
282 BALLISTIC MISSI LE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 299 and 300:
284 cos _':1'_ BALLISTIC MISSILE TR
- Page 301 and 302:
286 BALLISTIC MISSI LE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 303 and 304:
288 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 305 and 306:
290 °00 1 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJEC
- Page 307 and 308:
292 en 80 ... 0> Q) -0 .- EO c ..
- Page 309 and 310:
294 BALLISTIC MiSSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 311 and 312:
t tf EJ: :: I::/N!: :i : : : ! :x :
- Page 313 and 314:
298 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 315 and 316:
300 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 317 and 318:
302 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 319 and 320:
304 BALLISTIC MISSI LE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 321 and 322:
306 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 323 and 324:
308 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 325 and 326:
310 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 327 and 328:
312 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 329 and 330:
' 314 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIE
- Page 331 and 332:
316 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 333 and 334:
318 BA LLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 335 and 336:
320 BALLISTIC MISSILE TRAJECTORIES
- Page 337 and 338:
322 LUNAR TRAJECTO RIES Author in t
- Page 339 and 340:
324 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 Figure
- Page 341 and 342:
326 LUNAR TRAJECTOR I ES Ch. 7 Moon
- Page 343 and 344:
328 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 some a
- Page 345 and 346:
330 LUNAR TRAJECTO RIES Ch. 7 an in
- Page 347 and 348:
332 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 Figure
- Page 349 and 350:
334 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 where
- Page 351 and 352:
336 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch . 7 Figur
- Page 353 and 354:
338 LUNAR TRAJ ECTORIES Ch. 7 which
- Page 355 and 356:
340 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 number
- Page 357 and 358:
342 From equation (7.4-3) h = 1 .44
- Page 359 and 360:
344 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES eil. 7 From
- Page 361 and 362:
346 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch. 7 free f
- Page 363 and 364:
348 60 50 40 30 0 20 c «>- 10 0.
- Page 365 and 366:
350 - !3 o ::t: 1 h o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
- Page 367 and 368:
352 LUNAR TRAJECTOI;tIES Ch. 7 and
- Page 369 and 370:
354 LUNAR TRAJECTORIES Ch . 7 7.10
- Page 372 and 373:
CHAPTER 8 INTERPLANETARY TRAJECTORI
- Page 374 and 375:
Sec. 8.2 Planet Mercury Venus Earth
- Page 376 and 377:
.., 00 t Orbital Mean Planet Perio
- Page 378 and 379:
Sec. 8.3 \ THE PATCHED-CONIC APPROX
- Page 380 and 381:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHED-CONIC APPROXIM
- Page 382 and 383:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHED·CONIC APPROXI
- Page 384 and 385:
Sec. 8.3 to sun .-_.... THE PATCHED
- Page 386 and 387:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHED-CONIC APPROXIM
- Page 388 and 389:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHED-CONIC APPROXIM
- Page 390 and 391:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHE D·CONIC APPROX
- Page 392 and 393:
Sec. 8.3 THE PATCHED·CONIC APPROXI
- Page 394 and 395:
Sec. 8.4 NONCOPlANAR TRAJECTORIES V
- Page 396 and 397:
Ch. 8 EXERCISES 381 Show that or 3
- Page 398 and 399:
Ch. 8 EXERCISES 383 c. Find the vel
- Page 400 and 401:
CHAPTER 9 PERTURBATIONS "Life itsel
- Page 402 and 403:
Sec. 9.2 COWELL'S METHOD 387 contro
- Page 404 and 405:
Sec. 9.2 COWELL'S METHOD r=v • il
- Page 406 and 407:
Sec. 9.3 ENCKE'S METHOD 391 orbit.
- Page 408 and 409:
Sec. 9.3 ENCKE'S METHOD - - - Refer
- Page 410 and 411:
Sec. 9.3 ENCKE'S METHOD 395 which i
- Page 412 and 413:
Sec. 9.4 VAR IATION OF PARAMETERS O
- Page 414 and 415:
Sec. 9.4 VAR IAT ION OF PARAMETERS
- Page 416 and 417:
Sec. 9.4 VAR IATION OF PARAMETERS O
- Page 418 and 419:
Sec. 9.4 VARIAT ION OF PARAMETERS O
- Page 420 and 421:
Sec. 9.4 VAR iATiON OF PARAMETERES
- Page 422 and 423:
Sec. 9.4 VARIATION OF PARAMETERS OR
- Page 424 and 425:
Sec. 9.4 VARIATION OF PARAMETERS OR
- Page 426 and 427:
Sec. 9.4 VAR IATION OF PARAMETERS O
- Page 428 and 429:
Sec. 9.5 INTEGRATION SCHEMES AND ER
- Page 430 and 431:
Sec. 9.6 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METH
- Page 432 and 433:
Sec. 9.6 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METH
- Page 434 and 435:
Sec. 9.6 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METH
- Page 436 and 437:
Sec. 9.7 PERTURBATIVE ACCELERATIONS
- Page 438 and 439:
Sec. 9.7 PERTURBAT IVE ACCELERATION
- Page 440 and 441:
Ch. 9 EXERCISES where f = -4.5 X 10
- Page 442:
Ch. 9 EXERCISES 427 7. Townsend, G.
- Page 445 and 446:
APPENDIX B MISCELLANEOUS CONSTANTS
- Page 447 and 448:
432 VECTOR REVIEW C Equality of Vec
- Page 449 and 450:
434 (a) A-B = B A - (b) A -(B + C)
- Page 451 and 452:
436 VECTOR REVIEW (d) If A=A I I +
- Page 453 and 454:
438 x VECTO R REVI EW z K o .... ..
- Page 455 and 456:
APPENDIX D SUGGESTED PROJECTS This
- Page 457 and 458:
442 SUGGESTED PROJECTS D D.2 PROJEC
- Page 459 and 460:
444 Data Set 1 VI 0 VJ 0 VI( 1 DT 1
- Page 461 and 462:
446 SUGGESTED PROJECTS D procedures
- Page 463 and 464:
448 SUGGESTED PROJECTS D Launch Sit
- Page 466 and 467:
Acceleration comparison, 11 Adams-B
- Page 468 and 469:
Halley, Edmund, 2 Halley's comet, 2
- Page 470:
Rotating coordinate frame, 86-89 de